Transgenic expression of FoxM1 promotes endothelial repair following lung injury induced by polymicrobial sepsis in mice
- PMID: 23185540
- PMCID: PMC3502353
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050094
Transgenic expression of FoxM1 promotes endothelial repair following lung injury induced by polymicrobial sepsis in mice
Abstract
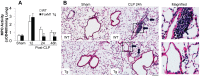
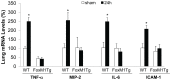
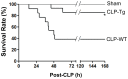
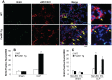
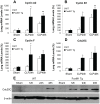
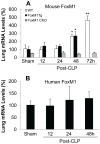
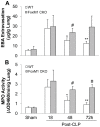
Enhancing endothelial barrier integrity for the treatment of acute lung injury (ALI) is an emerging novel therapeutic strategy. Our previous studies have demonstrated the essential role of FoxM1 in mediating endothelial regeneration and barrier repair following lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. However, it remains unclear whether FoxM1 expression is sufficient to promote endothelial repair in experimental models of sepsis. Here, employing the FoxM1 transgenic (FoxM1 Tg) mice, we showed that transgenic expression of FoxM1 promoted rapid recovery of endothelial barrier function and survival in a clinically relevant model of sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). We observed lung vascular permeability was rapidly recovered and returned to levels similar to baseline at 48 h post-CLP challenge in FoxM1 Tg mice whereas it remained markedly elevated in WT mice. Lung edema and inflammation were resolved only in FoxM1 Tg mice at 24 h post-CLP. 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine incorporation assay revealed a drastic induction of endothelial proliferation in FoxM1 Tg lungs at 24h post-CLP, correlating with early induction of expression of FoxM1 target genes essential for cell cycle progression. Additionally, deletion of FoxM1 in endothelial cells, employing the mouse model with endothelial cell-restricted disruption of FoxM1 (FoxM1 CKO) resulted in impaired endothelial repair following CLP challenge. Together, these data suggest FoxM1 expression in endothelial cells is necessary and sufficient to mediate endothelial repair and thereby promote survival following sepsis challenge.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
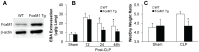
Similar articles
-
Endothelial Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Is Required for Vascular Repair and Resolution of Inflammatory Lung Injury through Forkhead Box Protein M1.Am J Pathol. 2019 Aug;189(8):1664-1679. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.04.014. Epub 2019 May 20. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31121134 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell-restricted disruption of FoxM1 impairs endothelial repair following LPS-induced vascular injury.J Clin Invest. 2006 Sep;116(9):2333-43. doi: 10.1172/JCI27154. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16955137 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial FoxM1 mediates bone marrow progenitor cell-induced vascular repair and resolution of inflammation following inflammatory lung injury.Stem Cells. 2014 Jul;32(7):1855-64. doi: 10.1002/stem.1690. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24578354 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple faces of FoxM1 transcription factor: lessons from transgenic mouse models.Cell Cycle. 2011 Feb 1;10(3):396-405. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.3.14709. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21270518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial TRPV4 channels in lung edema and injury.Curr Top Membr. 2022;89:43-62. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2022.07.001. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Curr Top Membr. 2022. PMID: 36210151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intratracheal Administration of Stem Cell Membrane-Cloaked Naringin-Loaded Biomimetic Nanoparticles Promotes Resolution of Acute Lung Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;13(3):282. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030282. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539816 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted roles of FOXM1 in pulmonary disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Apr 16;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0347-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30992007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial FoxM1 reactivates aging-impaired endothelial regeneration for vascular repair and resolution of inflammatory lung injury.Sci Transl Med. 2023 Aug 16;15(709):eabm5755. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abm5755. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Sci Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37585502 Free PMC article.
-
Rabeprazole Promotes Vascular Repair and Resolution of Sepsis-Induced Inflammatory Lung Injury through HIF-1α.Cells. 2022 Apr 22;11(9):1425. doi: 10.3390/cells11091425. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563731 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of FoxM1 Enhanced the Protective Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury through the Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Feb 11;2023:8324504. doi: 10.1155/2023/8324504. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36820407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, et al. (1998) Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood 91: 3527–3561. - PubMed
-
- Dejana E (2004) Endothelial cell-cell junctions: happy together. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 261–270. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100: 158–173. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA (2000) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342: 1334–1349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

