Vasculogenic mimicry of HT1080 tumour cells in vivo: critical role of HIF-1α-neuropilin-1 axis
- PMID: 23185562
- PMCID: PMC3504006
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050153
Vasculogenic mimicry of HT1080 tumour cells in vivo: critical role of HIF-1α-neuropilin-1 axis
Abstract
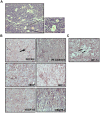
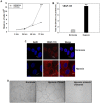
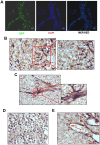
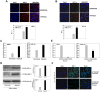
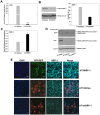
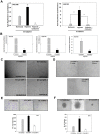
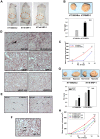
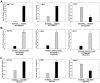
HT1080 - a human fibrosarcoma-derived cell line - forms aggressive angiogenic tumours in immuno-compromised mice. In spite of its extensive use as a model of tumour angiogenesis, the molecular event(s) initiating the angiogenic program in these cells are not known. Since hypoxia stimulates tumour angiogenesis, we examined the hypoxia-induced events evoked in these cells. In contrast to cells grown under normoxic conditions, hypoxia-primed (1% O(2)) HT1080 cells formed robust tubules on growth factor-reduced matrigel and formed significantly larger tumours in xenograft models in a chetomin-sensitive manner, indicating the role of HIF-1α-mediated transcription in these processes. Immuno-histochemical analyses of tumours formed by GFP-expressing HT1080 cells clearly showed that the tumour cells themselves expressed various angiogenic markers including Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) and formed functional vessels containing red blood cells, thereby unambiguously demonstrating the vasculogenic mimicry of HT1080 cells in vivo. Experiments performed with the HT1080 cells stably transfected with plasmid constructs expressing shNRP-1 or full-length NRP-1 clearly established that the HIF1α-mediated up-regulation of NRP-1 played a deterministic role in the process. Hypoxia-exposure resulted in an up-regulation of c-Myc and OCT3/4 and a down-regulation of KLF4 mRNAs, suggesting their involvement in the tumour formation and angiogenesis. However, silencing of NRP-1 alone, though not affecting proliferation in culture, was sufficient to abrogate the tumour formation completely; clearly establishing that the hypoxia-mediated HIF-1α-dependent up-regulation of NRP-1 is a critical molecular event involved in the vasculogenic mimicry and tumor formation by HT1080 cells in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of hypoxia-related gene expression in sarcomas and effect of hypoxia on RNA interference of vascular endothelial cell growth factor A.Cancer Res. 2005 Jul 1;65(13):5881-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4078. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15994966
-
HIF-1α induces VE-cadherin expression and modulates vasculogenic mimicry in esophageal carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 21;20(47):17894-904. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17894. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25548487 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of HIF-1 inhibition by chetomin on hypoxia-related transcription and radiosensitivity in HT 1080 human fibrosarcoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2007 Nov 13;7:213. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-213. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17999771 Free PMC article.
-
HIF and c-Myc: sibling rivals for control of cancer cell metabolism and proliferation.Cancer Cell. 2007 Aug;12(2):108-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.006. Cancer Cell. 2007. PMID: 17692803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of redox signaling in HIF-1-dependent tumor angiogenesis.FEBS J. 2022 Sep;289(18):5413-5425. doi: 10.1111/febs.16110. Epub 2021 Jul 16. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34228878 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-shaped vascular niche for cancer stem cells.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2015;19(1A):A39-43. doi: 10.5114/wo.2014.47130. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2015. PMID: 25691820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hypoxic microenvironment: a driving force for heterotopic ossification progression.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Feb 7;18(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-0509-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32028956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D collagen architecture induces a conserved migratory and transcriptional response linked to vasculogenic mimicry.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 21;8(1):1651. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01556-7. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29162797 Free PMC article.
-
Desmoglein 2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry in melanoma and is associated with poor clinical outcome.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):46492-46508. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10216. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27340778 Free PMC article.
-
Vasculogenic Mimicry: A Promising Prognosticator in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Esophageal Cancer? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cells. 2020 Feb 24;9(2):507. doi: 10.3390/cells9020507. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32102317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other Diseases. Nature. 407(6801): 249–257. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J (1995) Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 333(26): 1757–1763. - PubMed
-
- Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2011) Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med. 17(11): 1359–1370. - PubMed
-
- Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Seftor E, et al. (2000) Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene expression profiling. Nature 406(6795): 536–540. - PubMed
-
- Alitalo K, Carmeliet P (2002) Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell 1(3): 219–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

