Cerebrospinal fluid matrix metalloproteinases are elevated in cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy and correlate with MRI severity and neurologic dysfunction
- PMID: 23185624
- PMCID: PMC3503955
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050430
Cerebrospinal fluid matrix metalloproteinases are elevated in cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy and correlate with MRI severity and neurologic dysfunction
Abstract
Background: X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy results from mutations in the ABCD1 gene disrupting the metabolism of very-long-chain fatty acids. The most serious form of ALD, cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (cALD), causes neuroinflammation and demyelination. Neuroimaging in cALD shows inflammatory changes and indicates blood-brain-barrier (BBB) disruption. We hypothesize that disruption may occur through the degradation of the extracellular matrix defining the BBB by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). MMPs have not been evaluated in the setting of cALD.
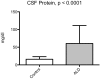
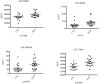
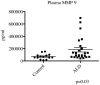
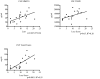
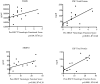
Methodology/principal findings: We used a multiplex assay to correlate the concentration of MMPs in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma to the severity of brain inflammation as determined by the ALD MRI (Loes) score and the neurologic function score. There were significant elevations of MMP2, MMP9, MMP10, TIMP1, and total protein in the CSF of boys with cALD compared to controls. Levels of MMP10, TIMP1, and total protein in CSF showed significant correlation [p<0.05 for each with pre-transplant MRI Loes Loes scores (R(2) = 0.34, 0.20, 0.55 respectively). Levels of TIMP1 and total protein in CSF significantly correlated with pre-transplant neurologic functional scores (R(2) = 0.22 and 0.48 respectively), and levels of MMP10 and total protein in CSF significantly correlated with one-year post-transplant functional scores (R(2) = 0.38 and 0.69). There was a significant elevation of MMP9 levels in plasma compared to control, but did not correlate with the MRI or neurologic function scores.
Conclusions/significance: MMPs were found to be elevated in the CSF of boys with cALD and may mechanistically contribute to the breakdown of the blood-brain-barrier. MMP concentrations directly correlate to radiographic and clinical neurologic severity. Interestingly, increased total protein levels showed superior correlation to MRI score and neurologic function score before and at one year after transplant.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Peters C (2004) Cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: the international hematopoietic cell transplantation experience from 1982 to 1999. Blood 104: 881–888. - PubMed
-
- Paintlia AS, Gilg AG, Khan M, Singh AK, Barbosa E, et al. (2003) Correlation of very long chain fatty acid accumulation and inflammatory disease progression in childhood X-ALD: implications for potential therapies. Neurobiol Dis 14: 425–439. - PubMed
-
- Deon M, Wajner M, Sirtori L, Fitarelli D, Coelho D, et al. (2006) The effect of Lorenzo's oil on oxidative stress in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 247: 157–164. - PubMed
-
- Lepperta D, Lindbergb RLP, Kapposa L, Leibc SL (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases: multifunctional effectors of inflammation in multiple sclerosis and bacterial meningitis. Brain Research Reviews 36: 249–257. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

