Role of predisposition, injury, response and organ failure in the prognosis of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 23186071
- PMCID: PMC3672612
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11882
Role of predisposition, injury, response and organ failure in the prognosis of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Acute deterioration of cirrhosis is associated with high mortality rates particularly in the patients who develop organ failure (OF), a condition that is referred to as acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), which is currently not completely defined. This study aimed to determine the role of predisposing factors, the nature of the precipitating illness and inflammatory response in the progression to OF according to the PIRO (predisposition, injury, response, organ failure) concept to define the risk of in-hospital mortality.
Methods: A total of 477 patients admitted with acute deterioration of cirrhosis following a defined precipitant over a 5.5-year period were prospectively studied. Baseline clinical, demographic and biochemical data were recorded for all patients and extended serial data from the group that progressed to OF were analysed to define the role of PIRO in determining in-hospital mortality.
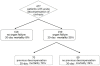
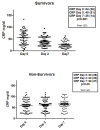
Results: One hundred and fifty-nine (33%) patients developed OF, of whom 93 patients died (58%) compared with 25/318 (8%) deaths in the non-OF group (P < 0.0001). Progression to OF was associated with more severe underlying liver disease and inflammation. In the OF group, previous hospitalisation (P of PIRO); severity of inflammation and lack of its resolution (R of PIRO); and severity of organ failure (O of PIRO) were associated with significantly greater risk of death. In the patients who recovered from OF, mortality at three years was almost universal.
Conclusions: The results of this prospective study shows that the occurrence of OF alters the natural history of cirrhosis. A classification based on the PIRO concept may allow categorization of patients into distinct pathophysiologic and prognostic groups and allow a multidimensional definition of ACLF.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Projections of mortality and burden of disease to 2030. Geneva: World Health Organization Press; 2004.
-
- Neuberger J, James O. Guidelines for selection of patients for liver transplantation in the era of donor-organ shortage. Lancet. 1999;16:1636–1639. - PubMed
-
- Duseja A, Chawla YK, Dhiman RK, Kumar A, Choudhary N, Taneja S. Non-hepatic insults are common acute precipitants in patients with acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF) Dig Dis Sci. 2010;16:3188–3192. - PubMed
-
- Sarin SK, Kumar A, Almeida JA, Chawla YK, Fan ST, Garg H, de Silva HJ, Hamid SS, Jalan R, Komolmit P, Lau GK, Liu Q, Madan K, Mohamed R, Ning Q, Rahman S, Rastogi A, Riordan SM, Sakhuja P, Samuel D, Shah S, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Takikawa Y, Thapa BR, Wai CT, Yuen MF. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the study of the liver (APASL) Hepatol Int. 2009;16:269–282. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sen S, Williams R, Jalan R. The pathophysiological basis of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver. 2002;16(Suppl 2):5–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

