Alterations in hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotidegated cation channel (HCN) expression in the hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus
- PMID: 23187002
- PMCID: PMC4133809
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2012.45.11.091
Alterations in hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotidegated cation channel (HCN) expression in the hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus
Abstract
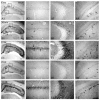
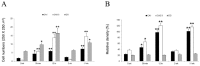
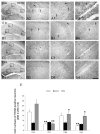
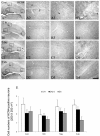
To understand the effects of HCN as potential mediators in the pathogenesis of epilepsy that evoke long-term impaired excitability; the present study was designed to elucidate whether the alterations of HCN expression induced by status epilepticus (SE) is responsible for epileptogenesis. Although HCN1 immunoreactivity was observed in the hippocampus, its immunoreactivities were enhanced at 12 hrs following SE. Although, HCN1 immunoreactivities were reduced in all the hippocampi at 2 weeks, a re-increase in the expression at 2-3 months following SE was observed. In contrast to HCN1, HCN 4 expressions were un-changed, although HCN2 immunoreactive neurons exhibited some changes following SE. Taken together, our findings suggest that altered expressions of HCN1 following SE may be mainly involved in the imbalances of neurotransmissions to hippocampal circuits; thus, it is proposed that HCN1 may play an important role in the epileptogenic period as a compensatory response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid loss of dendritic HCN channel expression in hippocampal pyramidal neurons following status epilepticus.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 5;31(40):14291-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1148-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21976514 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of a specific hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel (HCN) in surviving dentate gyrus granule cells of human and experimental epileptic hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 30;23(17):6826-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06826.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12890777 Free PMC article.
-
HCN Channel Phosphorylation Sites Mapped by Mass Spectrometry in Human Epilepsy Patients and in an Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Neuroscience. 2021 Apr 15;460:13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.01.038. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 33571596 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Altered HCN1 Expression on Brain Function and Its Relationship with Epileptogenesis.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(10):2070-2078. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230214110333. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37366350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HCN channelopathies: pathophysiology in genetic epilepsy and therapeutic implications.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;165(1):49-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01507.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21615728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Light-Driven Sodium Pump as a Potential Tool for the Control of Seizures in Epilepsy.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4691-4704. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03865-z. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38114761
-
The GABAB receptor associates with regulators of G-protein signaling 4 protein in the mouse prefrontal cortex and hypothalamus.BMB Rep. 2014 Jun;47(6):324-9. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2014.47.6.162. BMB Rep. 2014. PMID: 24286319 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 regulates hippocampal CA1 region excitability in rats with status epilepticus by suppressing the HCN1 channel.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Mar;18(3):594-602. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.350206. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36018183 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 Inhibition Prior to Status Epilepticus Persistently Enhances KCa2 Function in CA1 Which Slows Down Disease Progression.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Feb 26;14:33. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00033. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32174814 Free PMC article.
-
Improved HCN channels in pyramidal neurons and their new expression levels in pericytes and astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 subfield following transient ischemia.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Nov;44(5):1801-1810. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4353. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31573045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathern G. W., Babb T. L., Pretorius J. K., Melendez M., Levesque M. F. The pathophysiologic relationships between lesion pathology, intracranial ictal EEG onsets, and hippocampal neuron losses in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. (1995);21:133–147. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(95)00014-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

