RNA interference can be used to disrupt gene function in tardigrades
- PMID: 23187800
- PMCID: PMC3600081
- DOI: 10.1007/s00427-012-0432-6
RNA interference can be used to disrupt gene function in tardigrades
Abstract
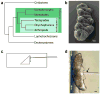
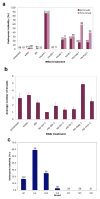
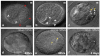
How morphological diversity arises is a key question in evolutionary developmental biology. As a long-term approach to address this question, we are developing the water bear Hypsibius dujardini (Phylum Tardigrada) as a model system. We expect that using a close relative of two well-studied models, Drosophila (Phylum Arthropoda) and Caenorhabditis elegans (Phylum Nematoda), will facilitate identifying genetic pathways relevant to understanding the evolution of development. Tardigrades are also valuable research subjects for investigating how organisms and biological materials can survive extreme conditions. Methods to disrupt gene activity are essential to each of these efforts, but no such method yet exists for the Phylum Tardigrada. We developed a protocol to disrupt tardigrade gene functions by double-stranded RNA-mediated RNA interference (RNAi). We showed that targeting tardigrade homologs of essential developmental genes by RNAi produced embryonic lethality, whereas targeting green fluorescent protein did not. Disruption of gene functions appears to be relatively specific by two criteria: targeting distinct genes resulted in distinct phenotypes that were consistent with predicted gene functions and by RT-PCR, RNAi reduced the level of a target mRNA and not a control mRNA. These studies represent the first evidence that gene functions can be disrupted by RNAi in the phylum Tardigrada. Our results form a platform for dissecting tardigrade gene functions for understanding the evolution of developmental mechanisms and survival in extreme environments.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microinjection of dsRNA in Tardigrades.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018 Nov 1;2018(11):10.1101/pdb.prot102368. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot102368. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018. PMID: 30385674 Free PMC article.
-
The Emergence of the Tardigrade Hypsibius exemplaris as a Model System.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018 Nov 1;2018(11). doi: 10.1101/pdb.emo102301. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018. PMID: 30385668 Review.
-
Comparative genomics of the tardigrades Hypsibius dujardini and Ramazzottius varieornatus.PLoS Biol. 2017 Jul 27;15(7):e2002266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2002266. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28749982 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative myoanatomy of Tardigrada: new insights from the heterotardigrades Actinarctus doryphorus (Tanarctidae) and Echiniscoides sigismundi (Echiniscoididae).BMC Evol Biol. 2019 Nov 6;19(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1527-8. BMC Evol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31694520 Free PMC article.
-
Miniaturization of tardigrades (water bears): Morphological and genomic perspectives.Arthropod Struct Dev. 2019 Jan;48:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.asd.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Arthropod Struct Dev. 2019. PMID: 30447338 Review.
Cited by
-
The Future of Cell Biology: Emerging Model Organisms.Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Nov;26(11):818-824. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27639630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations on the TardiVec-based analyses of tissue specificity and desiccation-induced supramolecular structure of target proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 28;120(48):e2312563120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2312563120. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37983508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Defining the viability of tardigrades with a molecular sensor related to death.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 26;13(10):e0206444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206444. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30365540 Free PMC article.
-
The tardigrade Hypsibius exemplaris dramatically upregulates DNA repair pathway genes in response to ionizing radiation.Curr Biol. 2024 May 6;34(9):1819-1830.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.03.019. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 38614079 Free PMC article.
-
Microinjection of dsRNA in Tardigrades.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018 Nov 1;2018(11):10.1101/pdb.prot102368. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot102368. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018. PMID: 30385674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguinaldo AM, Turbeville JM, Linford LS, Rivera MC, Garey JR, Raff RA, Lake JA. Evidence for a clade of nematodes, arthropods and other moulting animals. Nature. 1997;387:489–493. - PubMed
-
- Ahringer J Research Community, editor. The C. elegans. WormBook; 2006. Reverse genetics. - DOI
-
- Ammermann D. Die Cytologie der Parthenogenese bei dem Tardigraden Hypsibius dujardini. Chromosoma. 1967;23:203–213. - PubMed
-
- Benton R, Palacios IM, St Johnston D. Drosophila 14–3–3/PAR-5 is an essential mediator of PAR-1 function in axis formation. Dev Cell. 2002;3:659–671. - PubMed
-
- Bertolani R. Reproductive Biology of Invertebrates. I. John Wiley & Sons; Chichester: 1983. Tardigrades; pp. 431–441.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

