The CD39-adenosinergic axis in the pathogenesis of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 23188420
- PMCID: PMC3646120
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-012-9342-3
The CD39-adenosinergic axis in the pathogenesis of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
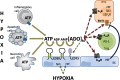
Hypoxic injury occurs when the blood supply to an organ is interrupted; subsequent reperfusion halts ongoing ischemic damage but paradoxically leads to further inflammation. Together this is termed ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). IRI is inherent to organ transplantation and impacts both the short- and long-term outcomes of the transplanted organ. Activation of the purinergic signalling pathway is intrinsic to the pathogenesis of, and endogenous response to IRI. Therapies targeting the purinergic pathway in IRI are an attractive avenue for the improvement of transplant outcomes and the basis of ongoing research. This review aims to examine the role of adenosine receptor signalling and the ecto-nucleotidases, CD39 and CD73, in IRI, with a particular focus on renal IRI.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

