Canonical transient receptor channel 5 (TRPC5) and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms
- PMID: 23188715
- PMCID: PMC3558807
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.112.082271
Canonical transient receptor channel 5 (TRPC5) and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms
Abstract
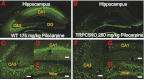
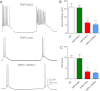
Seizures are the manifestation of highly synchronized burst firing of a large population of cortical neurons. Epileptiform bursts with an underlying plateau potential in neurons are a cellular correlate of seizures. Emerging evidence suggests that the plateau potential is mediated by neuronal canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) channels composed of members of the TRPC1/4/5 subgroup. We previously showed that TRPC1/4 double-knockout (DKO) mice lack epileptiform bursting in lateral septal neurons and exhibit reduced seizure-induced neuronal cell death, but surprisingly have unaltered pilocarpine-induced seizures. Here, we report that TRPC5 knockout (KO) mice exhibit both significantly reduced seizures and minimal seizure-induced neuronal cell death in the hippocampus. Interestingly, epileptiform bursting induced by agonists for metabotropic glutamate receptors in the hippocampal CA1 area is unaltered in TRPC5 KO mice, but is abolished in TRPC1 KO and TRPC1/4 DKO mice. In contrast, long-term potentiation is greatly reduced in TRPC5 KO mice, but is normal in TRPC1 KO and TRPC1/4 DKO mice. The distinct changes from these knockouts suggest that TRPC5 and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms. Furthermore, the reduced seizure and excitotoxicity and normal spatial learning exhibited in TRPC5 KO mice suggest that TRPC5 is a promising novel molecular target for new therapy.
Figures







References
-
- Alamed J, Wilcock DM, Diamond DM, Gordon MN, Morgan D. (2006) Two-day radial-arm water maze learning and memory task; robust resolution of amyloid-related memory deficits in transgenic mice. Nat Protoc 1:1671–1679 - PubMed
-
- Barton ME, Shannon HE. (2005) Behavioral and convulsant effects of the (S) enantiomer of the group I metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist 3,5-DHPG in mice. Neuropharmacology 48:779–787 - PubMed
-
- Birnbaumer L, Yildirim E, Abramowitz J. (2003) A comparison of the genes coding for canonical TRP channels and their M, V and P relatives. Cell Calcium 33:419–432 - PubMed
-
- Borges K, Gearing M, McDermott DL, Smith AB, Almonte AG, Wainer BH, Dingledine R. (2003) Neuronal and glial pathological changes during epileptogenesis in the mouse pilocarpine model. Exp Neurol 182:21–34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

