MR spectroscopic imaging: principles and recent advances
- PMID: 23188775
- PMCID: PMC11927461
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.23945
MR spectroscopic imaging: principles and recent advances
Abstract
MR spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) has become a valuable tool for quantifying metabolic abnormalities in human brain, prostate, breast and other organs. It is used in routine clinical imaging, particularly for cancer assessment, and in clinical research applications. This article describes basic principles of commonly used MRSI data acquisition and analysis methods and their impact on clinical applications. It also highlights technical advances, such as parallel imaging and newer high-speed MRSI approaches that are becoming viable alternatives to conventional MRSI methods. Although the main focus is on (1) H-MRSI, the principles described are applicable to other MR-compatible nuclei. This review of the state-of-the-art in MRSI methodology provides a framework for critically assessing the clinical utility of MRSI and for defining future technical development that is expected to lead to increased clinical use of MRSI. Future technical development will likely focus on ultra-high field MRI scanners, novel hyperpolarized contrast agents using metabolically active compounds, and ultra-fast MRSI techniques because these technologies offer unprecedented sensitivity and specificity for probing tissue metabolic status and dynamics.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures






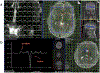



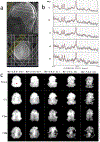
Similar articles
-
In vivo MR spectroscopic imaging of the prostate, from application to interpretation.Anal Biochem. 2017 Jul 15;529:158-170. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Anal Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28167072 Review.
-
Advances in MR spectroscopy of the prostate.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2008 Nov;16(4):697-710, ix-x. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2008.07.005. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2008. PMID: 18926432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developments in proton MR spectroscopic imaging of prostate cancer.MAGMA. 2022 Aug;35(4):645-665. doi: 10.1007/s10334-022-01011-9. Epub 2022 Apr 20. MAGMA. 2022. PMID: 35445307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An advanced MRI and MRSI data fusion scheme for enhancing unsupervised brain tumor differentiation.Comput Biol Med. 2017 Feb 1;81:121-129. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.12.017. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Comput Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28061367
-
Fast magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging techniques in human brain- applications in multiple sclerosis.J Biomed Sci. 2017 Feb 28;24(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12929-017-0323-2. J Biomed Sci. 2017. PMID: 28245815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance-Guided Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Radiotherapy on Combination MR-Linear Accelerators: Current Practice and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;15(7):2081. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072081. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echo-planar spectroscopic imaging with dual-readout alternated gradients (DRAG-EPSI) at 7 T: Application for 2-hydroxyglutarate imaging in glioma patients.Magn Reson Med. 2018 Apr;79(4):1851-1861. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26884. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Magn Reson Med. 2018. PMID: 28833542 Free PMC article.
-
WAND: Wavelet Analysis-Based Neural Decomposition of MRS Signals for Artifact Removal.NMR Biomed. 2025 Jun;38(6):e70038. doi: 10.1002/nbm.70038. NMR Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40289522 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated MR spectroscopic imaging-a review of current and emerging techniques.NMR Biomed. 2021 May;34(5):e4314. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4314. Epub 2020 May 12. NMR Biomed. 2021. PMID: 32399974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in clinical oncology.CA Cancer J Clin. 2021 Jul;71(4):333-358. doi: 10.3322/caac.21670. Epub 2021 May 13. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021. PMID: 33982817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maudsley AA, Hilal SK, Perman WH, Simon HE. Spatially resolved high resolution spectroscopy by “four-dimensional” NMR. J Magn Reson (1969) 1983;51:147–152.
-
- Yung KT, Zheng W, Zhao C, Martinez-Ramon M, van der Kouwe A, Posse S. Atlas-based automated positioning of outer volume suppression slices in short-echo time 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of the human brain. Magn Reson Med 2011;66:911–922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

