Thymic nurse cells provide microenvironment for secondary T cell receptor α rearrangement in cortical thymocytes
- PMID: 23188800
- PMCID: PMC3528577
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1213069109
Thymic nurse cells provide microenvironment for secondary T cell receptor α rearrangement in cortical thymocytes
Abstract
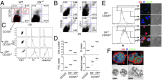
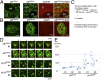
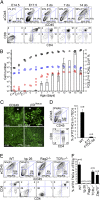
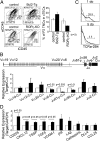
Distinct subsets of thymic epithelial cells (TECs) support T-cell development and selection. Isolated TECs contain multicellular complexes that enclose many viable thymocytes. However, the functions of those TECs, termed thymic nurse cells (TNCs), are unclear and the idea that TNCs are present in vivo is questioned. Here, we show that TNCs represent a fraction of cortical (c)TECs that are defined by the expression of thymoproteasomes. Intravital imaging revealed TNCs in the thymic cortex in situ, whereas TNCs were detected neither during embryogenesis nor in the postnatal thymuses of various "positive-selector" T-cell receptor (TCR)-transgenic mice, indicating that TNCs are not essential for T-cell differentiation, including positive selection. Rather, cells within TNCs were enriched for long-lived CD4(+)CD8(+) thymocytes that underwent secondary TCR-Vα rearrangement. Thus, TNC complexes are formed in vivo by persistent cTEC-thymocyte interactions that then provide a microenvironment that optimizes T-cell selection through secondary TCR rearrangement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bacci G. [Histochemical data on oocytes and nurse cells of Ophryotrocha puerilis.] Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1952;28(6):1293–1295. - PubMed
-
- Fritz IB. Reflections on the evolution of the regulation of spermatogenesis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;226:371–388. - PubMed
-
- Despommier DD. Trichinella spiralis and the concept of niche. J Parasitol. 1993;79(4):472–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

