Is central dogma a global property of cellular information flow?
- PMID: 23189060
- PMCID: PMC3505008
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00439
Is central dogma a global property of cellular information flow?
Abstract
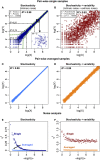
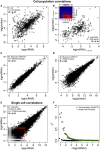
The central dogma of molecular biology has come under scrutiny in recent years. Here, we reviewed high-throughput mRNA and protein expression data of Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and several mammalian cells. At both single cell and population scales, the statistical comparisons between the entire transcriptomes and proteomes show clear correlation structures. In contrast, the pair-wise correlations of single transcripts to proteins show nullity. These data suggest that the organizing structure guiding cellular processes is observed at omics-wide scale, and not at single molecule level. The central dogma, thus, globally emerges as an average integrated flow of cellular information.
Keywords: biological noise; central dogma; correlation analysis; emergent behavior; gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Amati L., Guidorzi C., Frontera F., Della Valle K., Finelli F., Landi R., et al. (2008). Measuring the cosmological parameters with the Ep, i-Eiso correlation of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 391, 577–584
-
- Crick F. (1958). On protein synthesis. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 12, 139–163 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

