Role of therapeutic thoracentesis in tuberculous pleural effusion
- PMID: 23189098
- PMCID: PMC3506101
- DOI: 10.4103/1817-1737.102176
Role of therapeutic thoracentesis in tuberculous pleural effusion
Abstract
Context: Prevalence of tuberculous pleural effusion is very high in the Asian subcontinent but very few studies have come up from this part of the world about the course of recovery of pulmonary functions after institution of anti-tubercular therapy (ATT) and thoracentesis.
Aims: To study initial lung function impairment, changes over time after institution of ATT and thoracentesis and residual abnormalities left at the end of six months of treatment.
Settings and design: Randomized open level interventional study over two years in 52 patients at a tertiary level teaching hospital.
Methods: The study population was divided into two equal groups, A (therapeutic thoracentesis) and B (diagnostic thoracentesis). Spirometry, chest radiograph and ultrasonography of thorax were done initially and at each follow-up visit up to six months. Statistical analysis was done (P value < 0.05 considered significant).
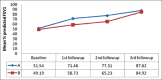
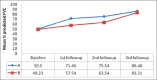
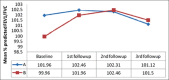
Results: Both groups were comparable initially. After six months none in group A and five patients in group B had minimal pleural effusion. During follow up, mean percentage predicted of FEV1 and FVC increased more in A than in B and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Pleural thickening, initially absent in both groups, was found to be more in B as compared to A at subsequent follow-up visits and this was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Thoracentesis should be considered in addition to anti-TB treatment, especially in large effusions, in order to relieve dyspnea, avoid possibility of residual pleural thickening and risk of developing restrictive functional impairment.
Keywords: Lung function; residual pleural thickening; thoracentesis; tuberculous pleural effusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Feller-Kopman D, Walky A, Berkowitz D, Ernst A. The relationship of pleural pressure to symptom development during therapeutic thoracentesis. Chest. 2006;129:1556–60. - PubMed
-
- Agusti AGN, Cardus J, Roca J, Grau JM, Xaubet A, Rodriguez-Roisin R. Ventilation-perfusion mismatch in patients of pleural effusion: Effects of thoracentesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(4 pt 1):1205–9. - PubMed
-
- Singla R. Pulmonary function tests in patients of tuberculous pleural effusion before, during and after chemotherapy. Ind J Tub. 1995;42:33–41.
-
- Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. ATS/ERS Task Force: Standardization of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005;26:319–38. - PubMed

