A Study on Work Ability Index and Physical Work Capacity on the Base of Fax Equation VO(2) Max in Male Nursing Hospital Staff in Isfahan, Iran
- PMID: 23189229
- PMCID: PMC3506089
A Study on Work Ability Index and Physical Work Capacity on the Base of Fax Equation VO(2) Max in Male Nursing Hospital Staff in Isfahan, Iran
Abstract
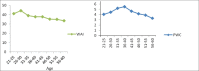
Background: The purpose of this research is to establish the ability of employees by work ability index (WAI), physical work capacity (PWC), and finding the correlation between them. Establishing the PWC index with attention to WAI values for the purpose of saving in costs and time of PWC measurements is another aim of this project.
Methods: The present research is an analytic cross-sectional and one-trail study. The study population consists of 228 randomly selected registered nurses from hospitals in Isfahan (Iran). The WAI and PWC were established through WAI questionnaire and Fax equation and by using ergometer bicycle, respectively. The resulting data were analyzed using SPSS 16 software.
Results: Average WAI and PWC among the study population were 38.25±4.4 and 4.45±0.7, respectively. Pearson test results showed no significant correlation between PWC and WAI in different age groups (r=0.3 and P>0.05). Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the variables of age and diagnosed diseases were the most effective factors of WAI (β=0.18 and P>0.05). Pearson test revealed a significant correlation between the number of diagnosed diseases and PWC index in age groups of 40-49 years.
Conclusion: Average WAI in this research, like other studies on similar jobs is in the acceptable level of >36. Work ability index and PWC index in different age groups did not show a significant correlation and this suggests that there are essential discrepancies in work ability evaluations made by each index and it is not possible to predict PWC index using WAI values. Given the PWC results and the level of nursing staff's activity (low, medium) the WAI is a suitable instrument to establish the professionals' abilities. This study revealed that 27.6% of individuals were subject to medium-low work ability risk (WAI<37), which was 1.8 times that of Finland's professional health Institute, which could be caused by shift working and increased working hours.
Keywords: Fax equation; hospital nurses; physical work capacity; work ability index.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors associated with work ability index (WAI) among intensive care units' (ICUs') nurses.J Occup Health. 2017 Mar 28;59(2):147-155. doi: 10.1539/joh.16-0060-OA. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Occup Health. 2017. PMID: 28077822 Free PMC article.
-
Work Ability Index (WAI) and its health-related determinants among Iranian farmers working in small farm enterprises.J Occup Health. 2014;56(6):478-84. doi: 10.1539/joh.13-0171-OA. Epub 2014 Oct 28. J Occup Health. 2014. PMID: 25355202
-
Work ability index (WAI) and its association with psychosocial factors in one of the petrochemical industries in Iran.J Occup Health. 2012;54(2):112-8. doi: 10.1539/joh.11-0150-oa. Epub 2012 Feb 14. J Occup Health. 2012. PMID: 22333439
-
Feasibility of physical training after myocardial infarction and its effect on return to work, morbidity and mortality.Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1976;599:7-84. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1976. PMID: 16981325 Review.
-
Worldwide prevalence of inadequate work ability among hospital nursing personnel: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2022 Jul;54(4):513-528. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12749. Epub 2021 Dec 16. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2022. PMID: 34918863
Cited by
-
Forced expiratory volume in one second: A novel predictor of work disability in subjects with suspected obstructive sleep apnea.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 19;13(7):e0201045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201045. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30024962 Free PMC article.
-
Demographic and occupational determinants of the work ability of firemen.J Occup Health. 2017 Jan 24;59(1):81-87. doi: 10.1539/joh.15-0296-FS. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Occup Health. 2017. PMID: 27916763 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the relationship between the aerobic capacity (VO2 max) and the rating of perceived exertion based on the measurement of heart beat in the metal industries Esfahan.J Educ Health Promot. 2014 Jun 23;3:55. doi: 10.4103/2277-9531.134751. eCollection 2014. J Educ Health Promot. 2014. PMID: 25077148 Free PMC article.
-
Subjective and Objective Evaluation Of Physical Activity Level And Its Relationship With Work Ability Of Nurses In Different Hospital Departments.Med Lav. 2025 Aug 4;116(4):15978. doi: 10.23749/mdl.v116i4.15978. Med Lav. 2025. PMID: 40762182 Free PMC article.
-
Precise Evaluation of Anthropometric 2D Software Processing of Hand in Comparison with Direct Method.J Med Signals Sens. 2013 Oct;3(4):256-61. J Med Signals Sens. 2013. PMID: 24696802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahonen G, Bjurström L, Hussi T, Räsänen K. Economic effectiveness of the maintenance and promotion of work ability. Maintenance of Work Ability-Research and Assessment: Summaries Bilbao: Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, Finnish Institute of Occupational Health. 2002:33–44.
-
- van den Berg TI, Elders LA, Burdorf A, editors. The effects of work-related and individual factors on work ability: A systematic review. Promotion of Work Ability towards Productive Aging: Selected papers of the 3rd International Symposium on Work Ability, Hanoi, Vietnam, 22-24 October 2007. 2008 CRC.
-
- Costa AF, Puga-Leal R, Nunes IL. An exploratory study of the Work Ability Index (WAI) and its components in a group of computer workers. Work. 2011;39:357–67. - PubMed
-
- Vigatto R, Alexandre NM, Correa Filho HR. Development of a Brazilian Portuguese version of the Oswestry Disability Index: cross-cultural adaptation, reliability, and validity. Spine. 2007;32:481–6. - PubMed
-
- Boedeker W. Associations between workload and diseases rarely occurring in sickness absence data. J Occup Environ Med. 2001;43:1081–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources