Autoproteolytic Activation of a Symbiosis-regulated Truffle Phospholipase A2
- PMID: 23192346
- PMCID: PMC3548466
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.384156
Autoproteolytic Activation of a Symbiosis-regulated Truffle Phospholipase A2
Abstract
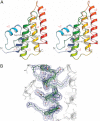
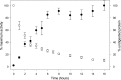
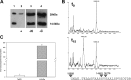
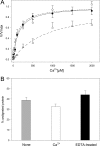
Fungal phospholipases are members of the fungal/bacterial group XIV secreted phospholipases A(2) (sPLA(2)s). TbSP1, the sPLA(2) primarily addressed in this study, is up-regulated by nutrient deprivation and is preferentially expressed in the symbiotic stage of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Tuber borchii. A peculiar feature of this phospholipase and of its ortholog from the black truffle Tuber melanosporum is the presence of a 54-amino acid sequence of unknown functional significance, interposed between the signal peptide and the start of the conserved catalytic core of the enzyme. X-ray diffraction analysis of a recombinant TbSP1 form corresponding to the secreted protein previously identified in T. borchii mycelia revealed a structure comprising the five α-helices that form the phospholipase catalytic module but lacking the N-terminal 54 amino acids. This finding led to a series of functional studies that showed that TbSP1, as well as its T. melanosporum ortholog, is a self-processing pro-phospholipase A(2), whose phospholipase activity increases up to 80-fold following autoproteolytic removal of the N-terminal peptide. Proteolytic cleavage occurs within a serine-rich, intrinsically flexible region of TbSP1, does not involve the phospholipase active site, and proceeds via an intermolecular mechanism. Autoproteolytic activation, which also takes place at the surface of nutrient-starved, sPLA(2) overexpressing hyphae, may strengthen and further control the effects of phospholipase up-regulation in response to nutrient deprivation, also in the context of symbiosis establishment and mycorrhiza formation.
Figures






References
-
- Murakami M., Taketomi Y., Miki Y., Sato H., Hirabayashi T., Yamamoto K. (2011) Recent progress in phospholipase A research. From cells to animals to humans. Prog. Lipid Res. 50, 152–192 - PubMed
-
- Drissner D., Kunze G., Callewaert N., Gehrig P., Tamasloukht M., Boller T., Felix G., Amrhein N., Bucher M. (2007) Lysophosphatidylcholine is a signal in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Science 318, 265–268 - PubMed
-
- Lee H. Y., Bahn S. C., Shin J. S., Hwang I., Back K., Doelling J. H., Ryu S. B. (2005) Multiple forms of secretory phospholipase A2 in plants. Prog. Lipid Res. 44, 52–67 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

