Predicting enhanced cell killing through PARP inhibition
- PMID: 23193155
- PMCID: PMC3552016
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0512
Predicting enhanced cell killing through PARP inhibition
Abstract
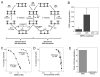
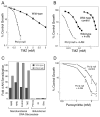
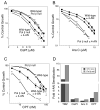
PARP inhibitors show promise as combination and single agents in cancer chemotherapy. Here, we evaluate results obtained with mouse fibroblasts and the common laboratory PARP inhibitor 4-amino-1,8-naphthalimide (4-AN) and analyze the potential for enhanced cytotoxicity following the combination of a DNA-damaging agent and a PARP inhibitor. Methylated DNA bases are repaired by the monofunctional glycosylase-initiated single-nucleotide base excision repair (BER) pathway. An intermediate of this process has a single-nucleotide gap in double-stranded DNA containing the 5'-deoxyribose phosphate (dRP) group at one margin. This 5'-dRP group is removed by the lyase activity of pol β prior to gap filling; then completion of repair is by DNA ligation. PARP-1 binds to and is activated by the 5'-dRP group-containing intermediate, and poly(ADP-ribos)ylation is important for efficient repair. 4-AN-mediated sensitization to the methylating chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide is extreme, producing a level of cytotoxicity not seen with either agent alone. In contrast, with agents producing oxidative DNA damage repaired by bifunctional glycosylase-initiated BER, there is only weak sensitization by cotreatment with PARP inhibitor. Other clinically used DNA-damaging agents repaired by different DNA repair pathways also reveal minimal 4-AN-mediated sensitization. This information has potentially important implications for strategic use of PARP inhibitors in chemotherapy.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Beard WA, Wilson SH. Structure and mechanism of DNA polymerase β. Chem Rev. 2006;106:361–82. - PubMed
-
- De Vos M, Schreiber V, Dantzer F. The diverse roles and clinical relevance of PARPs in DNA damage repair: Current state of the art. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84:137–46. - PubMed
-
- Lavrik OI, Prasad R, Sobol RW, Horton JK, Ackerman EJ, Wilson SH. Photoaffinity labeling of mouse fibroblast enzymes by a base excision repair intermediate. Evidence for the role of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 in DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:25541–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

