Islet α-, β-, and δ-cell development is controlled by the Ldb1 coregulator, acting primarily with the islet-1 transcription factor
- PMID: 23193182
- PMCID: PMC3581213
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0952
Islet α-, β-, and δ-cell development is controlled by the Ldb1 coregulator, acting primarily with the islet-1 transcription factor
Abstract
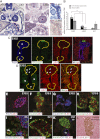
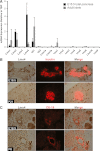
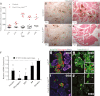
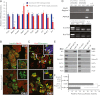
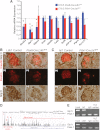
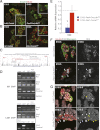
Ldb1 and Ldb2 are coregulators that mediate Lin11-Isl1-Mec3 (LIM)-homeodomain (HD) and LIM-only transcription factor-driven gene regulation. Although both Ldb1 and Ldb2 mRNA were produced in the developing and adult pancreas, immunohistochemical analysis illustrated a broad Ldb1 protein expression pattern during early pancreatogenesis, which subsequently became enriched in islet and ductal cells perinatally. The islet-enriched pattern of Ldb1 was similar to pan-endocrine cell-expressed Islet-1 (Isl1), which was demonstrated in this study to be the primary LIM-HD transcription factor in developing and adult islet cells. Endocrine cell-specific removal of Ldb1 during mouse development resulted in a severe reduction of hormone⁺ cell numbers (i.e., α, β, and δ) and overt postnatal hyperglycemia, reminiscent of the phenotype described for the Isl1 conditional mutant. In contrast, neither endocrine cell development nor function was affected in the pancreas of Ldb2(-/-) mice. Gene expression and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses demonstrated that many important Isl1-activated genes were coregulated by Ldb1, including MafA, Arx, insulin, and Glp1r. However, some genes (i.e., Hb9 and Glut2) only appeared to be impacted by Ldb1 during development. These findings establish Ldb1 as a critical transcriptional coregulator during islet α-, β-, and δ-cell development through Isl1-dependent and potentially Isl1-independent control.
Figures
References
-
- Slack JM. Developmental biology of the pancreas. Development 1995;121:1569–1580 - PubMed
-
- Pan FC, Wright C. Pancreas organogenesis: from bud to plexus to gland. Dev Dyn 2011;240:530–565 - PubMed
-
- Offield MF, Jetton TL, Labosky PA, et al. PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of the rostral duodenum. Development 1996;122:983–995 - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Cooper B, Gannon M, Ray M, MacDonald RJ, Wright CV. The role of the transcriptional regulator Ptf1a in converting intestinal to pancreatic progenitors. Nat Genet 2002;32:128–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007229/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK083160/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK078606/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY008126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-090570-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32-DK-083160/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60-DK-20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA-68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090570/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD-15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK-078606/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM-07229/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078606/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY-08126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

