UCNEbase--a database of ultraconserved non-coding elements and genomic regulatory blocks
- PMID: 23193254
- PMCID: PMC3531063
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1092
UCNEbase--a database of ultraconserved non-coding elements and genomic regulatory blocks
Abstract
UCNEbase (http://ccg.vital-it.ch/UCNEbase) is a free, web-accessible information resource on the evolution and genomic organization of ultra-conserved non-coding elements (UCNEs). It currently covers 4351 such elements in 18 different species. The majority of UCNEs are supposed to be transcriptional regulators of key developmental genes. As most of them occur as clusters near potential target genes, the database is organized along two hierarchical levels: individual UCNEs and ultra-conserved genomic regulatory blocks (UGRBs). UCNEbase introduces a coherent nomenclature for UCNEs reflecting their respective associations with likely target genes. Orthologous and paralogous UCNEs share components of their names and are systematically cross-linked. Detailed synteny maps between the human and other genomes are provided for all UGRBs. UCNEbase is managed by a relational database system and can be accessed by a variety of web-based query pages. As it relies on the UCSC genome browser as visualization platform, a large part of its data content is also available as browser viewable custom track files. UCNEbase is potentially useful to any computational, experimental or evolutionary biologist interested in conserved non-coding DNA elements in vertebrates.
Figures


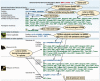

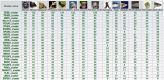
References
-
- Bejerano G, Pheasant M, Makunin I, Stephen S, Kent WJ, Mattick JS, Haussler D. Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science. 2004;304:1321–1325. - PubMed
-
- Dermitzakis ET, Reymond A, Lyle R, Scamuffa N, Ucla C, Deutsch S, Stevenson BJ, Flegel V, Bucher P, Jongeneel CV, et al. Numerous potentially functional but non-genic conserved sequences on human chromosome 21. Nature. 2002;420:578–582. - PubMed
-
- Elgar G, Vavouri T. Tuning in to the signals: noncoding sequence conservation in vertebrate genomes. Trends Genet. 2008;24:344–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

