KIDFamMap: a database of kinase-inhibitor-disease family maps for kinase inhibitor selectivity and binding mechanisms
- PMID: 23193279
- PMCID: PMC3531076
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1218
KIDFamMap: a database of kinase-inhibitor-disease family maps for kinase inhibitor selectivity and binding mechanisms
Abstract
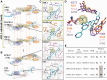
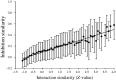
Kinases play central roles in signaling pathways and are promising therapeutic targets for many diseases. Designing selective kinase inhibitors is an emergent and challenging task, because kinases share an evolutionary conserved ATP-binding site. KIDFamMap (http://gemdock.life.nctu.edu.tw/KIDFamMap/) is the first database to explore kinase-inhibitor families (KIFs) and kinase-inhibitor-disease (KID) relationships for kinase inhibitor selectivity and mechanisms. This database includes 1208 KIFs, 962 KIDs, 55 603 kinase-inhibitor interactions (KIIs), 35 788 kinase inhibitors, 399 human protein kinases, 339 diseases and 638 disease allelic variants. Here, a KIF can be defined as follows: (i) the kinases in the KIF with significant sequence similarity, (ii) the inhibitors in the KIF with significant topology similarity and (iii) the KIIs in the KIF with significant interaction similarity. The KIIs within a KIF are often conserved on some consensus KIDFamMap anchors, which represent conserved interactions between the kinase subsites and consensus moieties of their inhibitors. Our experimental results reveal that the members of a KIF often possess similar inhibition profiles. The KIDFamMap anchors can reflect kinase conformations types, kinase functions and kinase inhibitor selectivity. We believe that KIDFamMap provides biological insights into kinase inhibitor selectivity and binding mechanisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Understanding kinase selectivity through energetic analysis of binding site waters.ChemMedChem. 2010 Apr 6;5(4):618-27. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900501. ChemMedChem. 2010. PMID: 20183853
-
Perspective on computational and structural aspects of kinase discovery from IPK2014.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1854(10 Pt B):1595-604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25861861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformation-selective inhibitors reveal differences in the activation and phosphate-binding loops of the tyrosine kinases Abl and Src.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):2734-43. doi: 10.1021/cb400663k. Epub 2013 Oct 29. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 24106839 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing protein kinase target similarity: Comparing sequence, structure, and cheminformatics approaches.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1854(10 Pt B):1605-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26001898
-
A structural atlas of kinases inhibited by clinically approved drugs.Methods Enzymol. 2014;548:23-67. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397918-6.00002-1. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 25399641 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring kinase family inhibitors and their moiety preferences using deep SHapley additive exPlanations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Jun 20;23(Suppl 4):242. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04760-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35725381 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational analysis of the DFG-out kinase motif and biochemical profiling of structurally validated type II inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 8;58(1):466-79. doi: 10.1021/jm501603h. Epub 2014 Dec 12. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25478866 Free PMC article.
-
Biomolecule and Bioentity Interaction Databases in Systems Biology: A Comprehensive Review.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 20;11(8):1245. doi: 10.3390/biom11081245. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KinaseMD: kinase mutations and drug response database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 8;49(D1):D552-D561. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa945. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33137204 Free PMC article.
-
Defining a new nomenclature for the structures of active and inactive kinases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 2;116(14):6818-6827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1814279116. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30867294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. Protein kinases—the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002;1:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Noble MEM, Endicott JA, Johnson LN. Protein kinase inhibitors: insights into drug design from structure. Science. 2004;303:1800–1805. - PubMed
-
- Weinmann H, Metternich R. Drug discovery process for kinase inhibitors. Chembiochem. 2005;6:455–459. - PubMed
-
- Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK, Gallant P, Atteridge CE, Campbell BT, Chan KW, Ciceri P, Davis MI, Edeen PT, et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:127–132. - PubMed

