Accuracy of plasma sTREM-1 for sepsis diagnosis in systemic inflammatory patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23194114
- PMCID: PMC3672614
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11884
Accuracy of plasma sTREM-1 for sepsis diagnosis in systemic inflammatory patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Early diagnosis of sepsis is vital to the clinical course and outcome of septic patients. Recently, soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) appears to be a potential marker of infection. The objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the accuracy of plasma sTREM-1 for sepsis diagnosis in systemic inflammatory patients.
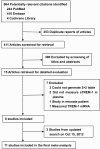
Methods: A systematic literature search of PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials was performed using specific search terms (up to 15 October 2012). Studies were included if they assessed the accuracy of plasma sTREM-1 for sepsis diagnosis in adult patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and provided sufficient information to construct a 2 X 2 contingency table.
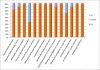
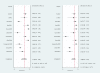
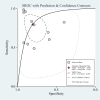
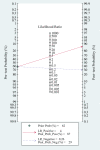
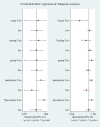
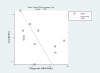
Results: Eleven studies with a total of 1,795 patients were included. The pooled sensitivity and specificity was 79% (95% confidence interval (CI), 65 to 89) and 80% (95% CI, 69 to 88), respectively. The positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio and diagnostic odds ratio were 4.0 (95% CI, 2.4 to 6.9), 0.26 (95% CI, 0.14 to 0.48), and 16 (95% CI, 5 to 46), respectively. The area under the curve of the summary receiver operator characteristic was 0.87 (95% CI, 0.84 to 0.89). Meta-regression analysis suggested that patient sample size and assay method were the main sources of heterogeneity. Publication bias was suggested by an asymmetrical funnel plot (P = 0.02).
Conclusions: The present meta-analysis showed that plasma sTREM-1 had a moderate diagnostic performance in differentiating sepsis from SIRS. Accordingly, plasma sTREM-1 as a single marker was not sufficient for sepsis diagnosis in systemic inflammatory patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of sTREM-1 in predicting mortality of infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2016 May 13;6(5):e010314. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010314. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27178971 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells in paediatric sepsis: a systematic review.Ital J Pediatr. 2016 Apr 27;42:44. doi: 10.1186/s13052-016-0242-y. Ital J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27116911 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Blood biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 1;2016(5):CD012179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012179. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27132058 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Current perspectives in the management of sepsis and septic shock.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 15;11:1431791. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1431791. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39211340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The accuracy assessment of presepsin (sCD14-ST) for mortality prediction in adult patients with sepsis and a head-to-head comparison to PCT: a meta-analysis.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019 Jun 13;15:741-753. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S198735. eCollection 2019. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019. PMID: 31354282 Free PMC article.
-
Role of sTREM-1 in predicting mortality of infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2016 May 13;6(5):e010314. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010314. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27178971 Free PMC article.
-
Are there new approaches for diagnosis, therapy guidance and outcome prediction of sepsis?World J Exp Med. 2015 May 20;5(2):50-63. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i2.50. eCollection 2015 May 20. World J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25992320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction.Open Life Sci. 2023 Aug 17;18(1):20220639. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0639. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37601077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pittet D, Rangel-Frausto S, Li N, Tarara D, Costigan M, Rempe L, Jebson P, Wenzel RP. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock: incidence, morbidities and outcomes in surgical ICU patients. Intensive Care Med. 1995;16:302–309. doi: 10.1007/BF01705408. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Otero RM, Nguyen HB, Huang DT, Gaieski DF, Goyal M, Gunnerson KJ, Trzeciak S, Sherwin R, Holthaus CV, Osborn T, Rivers EP. Early goal-directed therapy in severe sepsis and septic shock revisited: concepts, controversies, and contemporary findings. Chest. 2006;16:1579–1595. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.5.1579. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

