Regulation of intestinal serotonin transporter expression via epigenetic mechanisms: role of HDAC2
- PMID: 23195070
- PMCID: PMC3566538
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00361.2012
Regulation of intestinal serotonin transporter expression via epigenetic mechanisms: role of HDAC2
Abstract
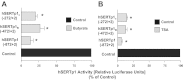
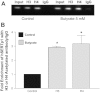
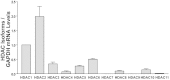
The serotonin (5-HT) transporter (SERT) facilitates clearance of extracellular 5-HT by its uptake and internalization. Decreased expression of SERT and consequent high 5-HT levels have been implicated in various diarrheal disorders. Thus, appropriate regulation of SERT is critical for maintenance of 5-HT homeostasis in health and disease. Previous studies demonstrated that SERT is regulated via posttranslational and transcriptional mechanisms. However, the role of epigenetic mechanisms in SERT regulation is not known. Current studies investigated the effects of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition on SERT expression and delineated the mechanisms. Treatment of Caco-2 cells with the pan-HDAC inhibitors butyrate (5 mM) and trichostatin (TSA, 1 μM) decreased SERT mRNA and protein levels. Butyrate- or TSA-induced decrease in SERT was associated with decreased activity of human SERT (hSERT) promoter 1 (upstream of exon 1a), but not hSERT promoter 2 (upstream of exon 2). Butyrate + TSA did not show an additive effect on SERT expression, indicating that mechanisms involving histone hyperacetylation may be involved. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated enrichment of the hSERT promoter 1 (flanking nt -250/+2) with tetra-acetylated histone H3 or H4, which was increased (~3-fold) by butyrate. Interestingly, specific inhibition of HDAC2 (but not HDAC1) utilizing small interfering RNA decreased SERT mRNA and protein levels. The decrease in SERT expression by HDAC inhibition was recapitulated in an in vivo model. SERT mRNA levels were decreased in the ileum and colon of mice fed pectin (increased availability of butyrate) compared with controls fed a fiber-free diet (~50-60%). Our results identify a novel role of HDAC2 as a regulator of SERT gene expression in intestinal epithelial cells.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Trichostatin A induces 5-lipoxygenase promoter activity and mRNA expression via inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 and 3.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Jul;16(7):1461-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01420.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21883892 Free PMC article.
-
CD1d induction in solid tumor cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors through inhibition of HDAC1/2 and activation of Sp1.Epigenetics. 2012 Apr;7(4):390-9. doi: 10.4161/epi.19373. Epub 2012 Apr 1. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22419072 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors stimulate mitochondrial HMG-CoA synthase gene expression via a promoter proximal Sp1 site.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Mar 15;31(6):1693-703. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg262. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12626711 Free PMC article.
-
[Epigenetic mechanisms and alcohol use disorders: a potential therapeutic target].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(1):83-91. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017014. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 28682229 Review. French.
-
Histone acetylation: molecular mnemonics on the chromatin.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Feb;14(2):97-111. doi: 10.1038/nrn3427. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23324667 Review.
Cited by
-
Connecting gut microbiomes and short chain fatty acids with the serotonergic system and behavior in Gallus gallus and other avian species.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 2;13:1035538. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1035538. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36406988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteroides ovatus colonization influences the abundance of intestinal short chain fatty acids and neurotransmitters.iScience. 2022 Mar 25;25(5):104158. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104158. eCollection 2022 May 20. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35494230 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Processing Sensitivity and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Japanese Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 11;19(16):9893. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19169893. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36011526 Free PMC article.
-
Looking Beyond the 5-HTTLPR Polymorphism: Genetic and Epigenetic Layers of Regulation Affecting the Serotonin Transporter Gene Expression.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Dec;54(10):8386-8403. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0304-6. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27933583 Review.
-
Infusion of donor feces affects the gut-brain axis in humans with metabolic syndrome.Mol Metab. 2020 Dec;42:101076. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101076. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32916306 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Alrefai WA, Wen X, Jiang W, Katz JP, Steinbrecher KA, Cohen MB, Williams IR, Dudeja PK, Wu GD. Molecular cloning and promoter analysis of downregulated in adenoma (DRA). Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 293: G923– G934, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bischoff SC, Mailer R, Pabst O, Weier G, Sedlik W, Li Z, Chen JJ, Murphy DL, Gershon MD. Role of serotonin in intestinal inflammation: knockout of serotonin reuptake transporter exacerbates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296: G685– G695, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bode KA, Dalpke AH. HDAC inhibitors block innate immunity. Blood 117: 1102– 1103, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK071596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-81858/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005243/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DK054016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-92441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-096258/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK096258/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-74458/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-71596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK074458/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-54016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000152/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

