Concise review: the role of clinical trials in deciphering mechanisms of action of cardiac cell-based therapy
- PMID: 23197637
- PMCID: PMC3727692
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2011-0014
Concise review: the role of clinical trials in deciphering mechanisms of action of cardiac cell-based therapy
Abstract
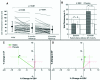
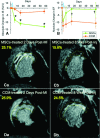
Although the initial promise of cardiac cell-based therapy was based on the concept that stem cells engraft into diseased tissue and differentiate into beating cardiomyocytes, it is now clear that successful cell-based tissue repair involves a more complex orchestration of cellular and molecular events. Many lessons about successful tissue repair can be gleaned from the results of early-stage clinical trials. This body of work shows that cell-based therapy (with various cell sources and delivery methods) effectively prevents and reverses the remodeling process, the sine qua non of the myocardial injury reaction and anatomic substrate for subsequent clinical events. The potentially favorable remodeling responses to cell therapy have prompted a search for mechanisms of action beyond cell repopulation and guided future clinical trial design by providing more clear focus on pathophysiological endpoints signifying favorable responses to cell-based therapy. Perhaps the most important mechanistic insight is that endogenous stem/precursor cells have the potential to participate in tissue healing. With regard to the phenotype of cellular response, it is clear that parameters of remodeling, such as infarct size and ventricular dimensions, should be directly measured, thereby necessitating the use of sophisticated imaging modalities, such as cardiac magnetic resonance imaging or multidetector computed tomography. These new insights offer an optimistic outlook on the state of cell-based therapeutics for cardiac disease and suggest that pivotal clinical trials are warranted. Here, we review lessons learned from clinical trials and evaluate the choice and assessment of endpoints to best predict efficacy of cell therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Selem S, Hatzistergos KE, Hare JM. Cardiac stem cells: Biology and therapeutic applications. In: Atala A, Lanza R, Thomson JA, editors. Principles of Regenerative Medicine. San Diego, CA: Elsevier Inc; 2011. pp. 327–346.
-
- Abdel-Latif A, Bolli R, Tleyjeh IM, et al. Adult bone marrow-derived cells for cardiac repair: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:989–997. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Rendon E, Brunskill SJ, Hyde CJ, et al. Autologous bone marrow stem cells to treat acute myocardial infarction: A systematic review. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:1807–1818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01-HL084275/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HL113460/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084275/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094849/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20-HL101443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL081028/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL107110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54-HL081028/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL094849/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 HL101443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

