Mechanisms generating dual-component nicotinic EPSCs in cortical interneurons
- PMID: 23197720
- PMCID: PMC3525105
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3565-12.2012
Mechanisms generating dual-component nicotinic EPSCs in cortical interneurons
Abstract
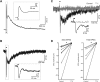
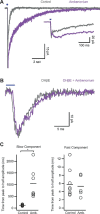
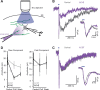
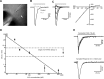
Activation of cortical nicotinic receptors by cholinergic axons from the basal forebrain (BF) significantly impacts cortical function, and the loss of nicotinic receptors is a hallmark of aging and neurodegenerative disease. We have previously shown that stimulation of BF axons generates a fast α7 and a slow non-α7 receptor-dependent response in cortical interneurons. However, the synaptic mechanisms that underlie this dual-component nicotinic response remain unclear. Here, we report that fast α7 receptor-mediated EPSCs in the mouse cortex are highly variable and insensitive to perturbations of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), while slow non-α7 receptor-mediated EPSCs are reliable and highly sensitive to AChE activity. Based on these data, we propose that the fast and slow nicotinic responses reflect differences in synaptic structure between cholinergic varicosities activating α7 and non-α7 classes of nicotinic receptors.
Figures

References
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Albuquerque EX. alpha-bungarotoxin- and methyllycaconitine-sensitive nicotinic receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in interneurons of rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1998;810:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Birks J, Harvey RJ. Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;2006:CD001190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
