A common rule for decision making in animal collectives across species
- PMID: 23197836
- PMCID: PMC3528575
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1210664109
A common rule for decision making in animal collectives across species
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 26;110(9):3651
Abstract
A diversity of decision-making systems has been observed in animal collectives. In some species, choices depend on the differences of the numbers of animals that have chosen each of the available options, whereas in other species on the relative differences (a behavior known as Weber's law), or follow more complex rules. We here show that this diversity of decision systems corresponds to a single rule of decision making in collectives. We first obtained a decision rule based on Bayesian estimation that uses the information provided by the behaviors of the other individuals to improve the estimation of the structure of the world. We then tested this rule in decision experiments using zebrafish (Danio rerio), and in existing rich datasets of argentine ants (Linepithema humile) and sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus), showing that a unified model across species can quantitatively explain the diversity of decision systems. Further, these results show that the different counting systems used by animals, including humans, can emerge from the common principle of using social information to make good decisions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
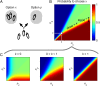
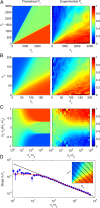
 . The rate of change of Px in the transition regions depends on the reliability parameter s, with the width of these regions proportional to
. The rate of change of Px in the transition regions depends on the reliability parameter s, with the width of these regions proportional to  . (C) Same as B but for three different values of parameter k: k = 0 (Left), 0 < k < 1 (Center), and k = 1 (Right).
. (C) Same as B but for three different values of parameter k: k = 0 (Left), 0 < k < 1 (Center), and k = 1 (Right).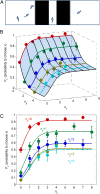
 and
and  . (D) Slope of the probability of choosing x in A as obtained from a linear fit along the lines depicted in Inset. Experimental values (blue dots; error bars are 95% confidence interval), theory (red line), and Weber’s law (black line).
. (D) Slope of the probability of choosing x in A as obtained from a linear fit along the lines depicted in Inset. Experimental values (blue dots; error bars are 95% confidence interval), theory (red line), and Weber’s law (black line).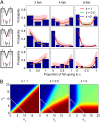
References
-
- Knill DC, Pouget A. The Bayesian brain: The role of uncertainty in neural coding and computation. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27(12):712–719. - PubMed
-
- Gold JI, Shadlen MN. The neural basis of decision making. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:535–574. - PubMed
-
- Tenenbaum JB, Kemp C, Griffiths TL, Goodman ND. How to grow a mind: Statistics, structure, and abstraction. Science. 2011;331(6022):1279–1285. - PubMed
-
- Biernaskie JM, Walker SC, Gegear RJ. Bumblebees learn to forage like Bayesians. Am Nat. 2009;174(3):413–423. - PubMed
-
- McNamara JM, Green RF, Olsson O. Bayes theorem and its applications in animal behaviour. Oikos. 2006;112(2):243–251.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

