Neural stem cell grafting counteracts hippocampal injury-mediated impairments in mood, memory, and neurogenesis
- PMID: 23197876
- PMCID: PMC3612501
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0050
Neural stem cell grafting counteracts hippocampal injury-mediated impairments in mood, memory, and neurogenesis
Abstract
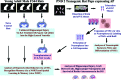
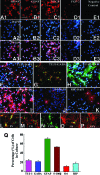
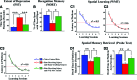
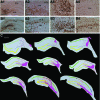
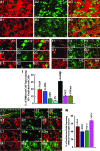
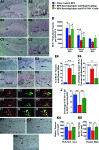
The hippocampus is vital for functions such as mood and memory. Hippocampal injury typically leads to mood and memory impairments associated with reduced and aberrant neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus. We examined whether neural stem cell (NSC) grafting after hippocampal injury would counteract impairments in mood, memory, and neurogenesis. We expanded NSCs from the anterior subventricular zone (SVZ) of postnatal F344 rat pups expressing the human placental alkaline phosphatase and grafted them into the hippocampus of young adult F344 rats at 5 days after an injury inflicted through a unilateral intracerebroventricular administration of kainic acid. Analyses through forced swim, water maze, and novel object recognition tests revealed significant impairments in mood and memory function in animals that underwent injury and sham-grafting surgery. In contrast, animals that received SVZ-NSC grafts after injury exhibited mood and memory function comparable to those of naïve control animals. Graft-derived cells exhibited excellent survival and pervasive migration, and they differentiated into neurons, subtypes of inhibitory GABAergic interneurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and oligodendrocyte progenitors. Significant fractions of graft-derived cells also expressed beneficial neurotrophic factors such as the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, fibroblast growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor. Furthermore, SVZ-NSC grafting counteracted the injury-induced reductions and abnormalities in neurogenesis by both maintaining a normal level of NSC activity in the subgranular zone and providing protection to reelin+ interneurons in the dentate gyrus. These results underscore that early SVZ-NSC grafting intervention after hippocampal injury is efficacious for thwarting mood and memory dysfunction and abnormal neurogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Kryukov VI. The role of the hippocampus in long-term memory: Is it memory store or comparator? J Integr Neurosci. 2008;7:117–184. - PubMed
-
- Samuels BA, Hen R. Neurogenesis and affective disorders. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;33:1152–1159. - PubMed
-
- Cohen AS, Pfister BJ, Schwarzbach E, et al. Injury-induced alterations in CNS electrophysiology. Prog Brain Res. 2007;161:143–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

