Dysphagia after colon interposition graft for esophageal carcinoma
- PMID: 23198233
- PMCID: PMC3502822
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/738205
Dysphagia after colon interposition graft for esophageal carcinoma
Abstract
Colon interposition is an established technique for esophageal reconstruction. We describe the case of primary adenocarcinoma arising in a colonic interposition graft that was performed after total esophagectomy for recurrence adenocarcinoma derived from the Barrett esophagus.
Figures
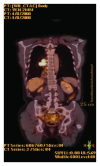
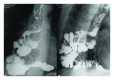
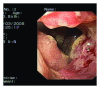

References
-
- Kelling GE. Oesophagoplastik mit hilfeder querkolon. Das Zentralblatt für Chirurgie. 1911;38:1209–1212.
-
- Vuillet H. De l'oesophagoplastiek et des diverses modifications. Semaine de la Méditerranée. 1911;31:529–534.
-
- Larson TC, Shuman LS, Libshitz HI, McMurtrey MJ. Complications of colonic interposition. Cancer. 1985;56(3):681–690. - PubMed
-
- Belsey R. Replacement of the Esophagus With the Colon. General Thoracic Surgery. 2000
-
- Postlethwait RW, Sealy WC, Dillon ML, Young WG. Colon interposition for esophageal substitution. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 1971;12(1):89–109. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

