Inflammatory cytokines as predictive markers for early detection and progression of diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 23199046
- PMCID: PMC3405301
- DOI: 10.1007/s13167-010-0004-7
Inflammatory cytokines as predictive markers for early detection and progression of diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
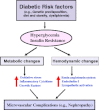
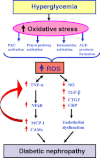
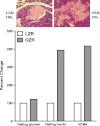
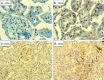
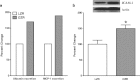
Diabetic nephropathy is a major complication of diabetes mellitus and the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Both hyperglycemia and hypertension (systemic and/or intraglomerular) are established causal factors for diabetic nephropathy. Nonetheless, there is growing evidence that activated innate immunity and inflammation are also contributing factors to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. This notion is based on increasing evidence indicating that both cytokines-chemokines and pro-fibrotic growth factors are important players in the progression of diabetic nephropathy, effectively accelerating and exacerbating inflammatory and fibrotic processes leading to end-stage renal disease. In this review, we focus on several predominant cytokines-chemokines as potential predictive markers for diabetic nephropathy. These cytokines-chemokines may also be helpful as biomarkers to monitor the progression of the disease and the impact of interventional modalities aimed at halting eventual manifestation of end-stage renal disease in diabetic patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation.World J Diabetes. 2014 Jun 15;5(3):393-8. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i3.393. World J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24936261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation and the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy.Clin Sci (Lond). 2013 Feb;124(3):139-52. doi: 10.1042/CS20120198. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23075333 Review.
-
Relationship between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy.Cardiovasc Ther. 2012 Feb;30(1):49-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00218.x. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Cardiovasc Ther. 2012. PMID: 20718759 Review.
-
Inflammation and diabetic nephropathy.Curr Diab Rep. 2006 Dec;6(6):463-8. doi: 10.1007/s11892-006-0080-1. Curr Diab Rep. 2006. PMID: 17118230 Review.
-
The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: focus on microRNAs and proteomics.J Nephrol. 2013 Sep-Oct;26(5):811-20. doi: 10.5301/jn.5000262. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23543479 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Systemic Inflammation Response Index with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Feb 1;17:517-531. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S447026. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38327734 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of single and persistent elevation of serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels for prediction of kidney outcomes in patients with impaired fasting glucose or diabetes mellitus.J Nephrol. 2021 Aug;34(4):1179-1188. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00848-4. Epub 2020 Sep 3. J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32880885
-
Circular RNA COL1A2 Mediates High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Pyroptosis by Regulating MiR-424-5p/SGK1 in Diabetic Nephropathy.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;195(12):7652-7667. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04501-1. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37079269 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and global research trends of immunity in diabetic nephropathy: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2004 to 2023.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Oct;56(10):3307-3321. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04081-x. Epub 2024 May 17. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38758346 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2022 Oct 15;6(6):536-551. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2022.09.002. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 36277502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

