Fatal respiratory distress syndrome due to coronavirus infection in a child with severe combined immunodeficiency
- PMID: 23199056
- PMCID: PMC5781196
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12059
Fatal respiratory distress syndrome due to coronavirus infection in a child with severe combined immunodeficiency
Abstract
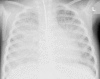
Coronaviruses have been demonstrated to contribute substantially to respiratory tract infections among the child population. Though infected children commonly present mild upper airway symptoms, in high-risk patients with underlying conditions, particularly in immunocompromised children these pathogens may lead to severe lung infection and extrapulmonary disorders. In this paper, we provide the first report of the case of a 15-month-old child with severe combined immunodeficiency and coronavirus HKU1-related pneumonia with fatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Keywords: Coronavirus; children; pneumonia; severe combined immunodeficiency.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Leukapheresis Depletion in an Ex-Premature with Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Due to Bordetella Pertussis and Coronavirus Infection.Blood Purif. 2020;49(6):758-760. doi: 10.1159/000507873. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Blood Purif. 2020. PMID: 32340021 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus HKU1 and other coronavirus infections in Hong Kong.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Jun;44(6):2063-71. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02614-05. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16757599 Free PMC article.
-
Human (non-severe acute respiratory syndrome) coronavirus infections in hospitalised children in France.J Paediatr Child Health. 2008 Apr;44(4):176-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2007.01246.x. Epub 2007 Nov 12. J Paediatr Child Health. 2008. PMID: 17999671 Free PMC article.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
-
Molecular biology of coronaviruses: an overview of virus-host interactions and pathogenesis.Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2021;78(1):41-58. doi: 10.24875/BMHIM.20000249. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2021. PMID: 33661875 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Coronavirus in Recent Years: Characteristics, Outbreaks, and Treatments.Tanaffos. 2024 Mar;23(3):220-237. Tanaffos. 2024. PMID: 40704343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What's New With the Old Coronaviruses?J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2020 Apr 30;9(2):210-217. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piaa037. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2020. PMID: 32314790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From SARS coronavirus to novel animal and human coronaviruses.J Thorac Dis. 2013 Aug;5 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S103-8. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.06.02. J Thorac Dis. 2013. PMID: 23977429 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus pneumonia as the first manifestation of severe combined immunodeficiency.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2014;39(3):392-5. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2014.45953. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 26155153 Free PMC article.
-
The Complexity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 10;13:789882. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.789882. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35222327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kahn JS. The widening scope of coronaviruses. Curr Opin Pediatr 2006; 18:42–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

