The GGGGCC repeat expansion in C9ORF72 in a case with discordant clinical and FDG-PET findings: PET trumps syndrome
- PMID: 23199140
- PMCID: PMC3593970
- DOI: 10.1080/13554794.2012.732090
The GGGGCC repeat expansion in C9ORF72 in a case with discordant clinical and FDG-PET findings: PET trumps syndrome
Abstract
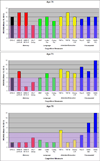
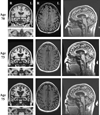
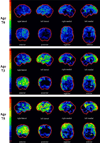
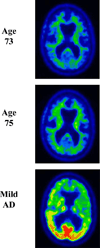
A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in the chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 (C9ORF72) gene was recently discovered as the cause underlying frontotemporal degeneration (FTD) and/or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) linked to chromosome 9 (c9FTD/ALS). In this atypical case of c9FTD/ALS, the proband presented with amnestic mild cognitive impairment which evolved into Alzheimer's disease (AD)-type dementia and later developed ALS. Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography of the brain demonstrated mild hypometabolism involving the medial frontal and lateral temporal lobes, left more so than right, which progressed over time. He was subsequently confirmed to have the C9ORF72 expansion. This report highlights the need to consider mutations in the FTD-associated genes when a familial disorder is suggested and neuroimaging studies reveal findings atypical of an AD pathophysiological process despite the typical anterograde amnestic syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 2006;351:602–611. - PubMed
-
- Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL. El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Other Motor Neuron Disorders. 2000;1:293–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
