Peanut oral immunotherapy modifies IgE and IgG4 responses to major peanut allergens
- PMID: 23199605
- PMCID: PMC3529994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.10.048
Peanut oral immunotherapy modifies IgE and IgG4 responses to major peanut allergens
Abstract
Background: Patients with peanut allergy have highly stable pathologic antibody repertoires to the immunodominant B-cell epitopes of the major peanut allergens Ara h 1 to 3.
Objective: We used a peptide microarray technique to analyze the effect of treatment with peanut oral immunotherapy (OIT) on such repertoires.
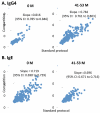
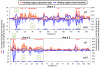
Methods: Measurements of total peanut-specific IgE (psIgE) and peanut-specific IgG(4) (psIgG(4)) were made with CAP-FEIA. We analyzed sera from 22 patients with OIT and 6 control subjects and measured serum specific IgE and IgG(4) binding to epitopes of Ara h 1 to 3 using a high-throughput peptide microarray technique. Antibody affinity was measured by using a competitive peptide microarray, as previously described.
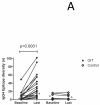
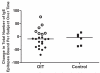
Results: At baseline, psIgE and psIgG(4) diversity was similar between patients and control subjects, and there was broad variation in epitope recognition. After a median of 41 months of OIT, polyclonal psIgG(4) levels increased from a median of 0.3 μg/mL (interquartile range [25% to 75%], 0.1-0.43 μg/mL) at baseline to 10.5 μg/mL (interquartile range [25% to 75%], 3.95-45.48 μg/mL; P < .0001) and included de novo specificities. psIgE levels were reduced from a median baseline of 85.45 kU(A)/L (23.05-101.0 kU(A)/L) to 7.75 kU(A)/L (2.58-30.55 kU(A)/L, P < .0001). Affinity was unaffected. Although the psIgE repertoire contracted in most OIT-treated patients, several subjects generated new IgE specificities, even as the total psIgE level decreased. Global epitope-specific shifts from IgE to IgG(4) binding occurred, including at an informative epitope of Ara h 2.
Conclusion: OIT differentially alters Ara h 1 to 3 binding patterns. These changes are variable between patients, are not observed in control subjects, and include a progressive polyclonal increase in IgG(4) levels, with concurrent reduction in IgE amount and diversity.
Copyright © 2012 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Clark AT, Islam S, King Y, Deighton J, Anagnostou K, Ewan PW. Successful oral tolerance induction in severe peanut allergy. Allergy. 2009 Aug;64(8):1218–20. - PubMed
-
- Blumchen K, Ulbricht H, Staden U, Dobberstein K, Beschorner J, de Oliveira LC, et al. Oral peanut immunotherapy in children with peanut anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Jul;126(1):83–91.e1. - PubMed
-
- Beyer K, Ellman-Grunther L, Järvinen KM, Wood RA, Hourihane J, Sampson HA. Measurement of peptide-specific IgE as an additional tool in identifying patients with clinical reactivity to peanuts. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112(1):202–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

