Thrombin activity propagates in space during blood coagulation as an excitation wave
- PMID: 23200057
- PMCID: PMC3512051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.10.011
Thrombin activity propagates in space during blood coagulation as an excitation wave
Abstract
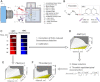
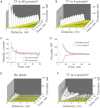
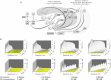
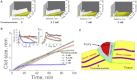
Injury-induced bleeding is stopped by a hemostatic plug formation that is controlled by a complex nonlinear and spatially heterogeneous biochemical network of proteolytic enzymes called blood coagulation. We studied spatial dynamics of thrombin, the central enzyme of this network, by developing a fluorogenic substrate-based method for time- and space-resolved imaging of thrombin enzymatic activity. Clotting stimulation by immobilized tissue factor induced localized thrombin activity impulse that propagated in space and possessed all characteristic traits of a traveling excitation wave: constant spatial velocity, constant amplitude, and insensitivity to the initial stimulation once it exceeded activation threshold. The parameters of this traveling wave were controlled by the availability of phospholipids or platelets, and the wave did not form in plasmas from hemophilia A or C patients who lack factors VIII and XI, which are mediators of the two principal positive feedbacks of coagulation. Stimulation of the negative feedback of the protein C pathway with thrombomodulin produced nonstationary patterns of wave formation followed by deceleration and annihilation. This indicates that blood can function as an excitable medium that conducts traveling waves of coagulation.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ataullakhanov F.I., Guria G.T., Volkova R.I. Spatiotemporal dynamics of clotting and pattern formation in human blood. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1425:453–468. - PubMed
-
- Zarnitsina V.I., Pokhilko A.V., Ataullakhanov F.I. A mathematical model for the spatio-temporal dynamics of intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. II. Results. Thromb. Res. 1996;84:333–344. - PubMed
-
- Loose M., Fischer-Friedrich E., Schwille P. Spatial regulators for bacterial cell division self-organize into surface waves in vitro. Science. 2008;320:789–792. - PubMed
-
- Ovanesov M.V., Ananyeva N.M., Saenko E.L. Initiation and propagation of coagulation from tissue factor-bearing cell monolayers to plasma: initiator cells do not regulate spatial growth rate. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005;3:321–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

