Muscle contributions to vertical and fore-aft accelerations are altered in subjects with crouch gait
- PMID: 23200083
- PMCID: PMC3600387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2012.10.019
Muscle contributions to vertical and fore-aft accelerations are altered in subjects with crouch gait
Abstract
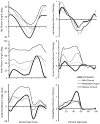
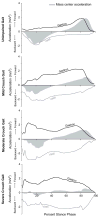
The goals of this study were to determine if the muscle contributions to vertical and fore-aft acceleration of the mass center differ between crouch gait and unimpaired gait and if these muscle contributions change with crouch severity. Examining muscle contributions to mass center acceleration provides insight into the roles of individual muscles during gait and can provide guidance for treatment planning. We calculated vertical and fore-aft accelerations using musculoskeletal simulations of typically developing children and children with cerebral palsy and crouch gait. Analysis of these simulations revealed that during unimpaired gait the quadriceps produce large upward and backward accelerations during early stance, whereas the ankle plantarflexors produce large upward and forward accelerations later in stance. In contrast, during crouch gait, the quadriceps and ankle plantarflexors produce large, opposing fore-aft accelerations throughout stance. The quadriceps force required to accelerate the mass center upward was significantly larger in crouch gait than in unimpaired gait and increased with crouch severity. The gluteus medius accelerated the mass center upward during midstance in unimpaired gait; however, during crouch gait the upward acceleration produced by the gluteus medius was significantly reduced. During unimpaired gait the quadriceps and ankle plantarflexors accelerate the mass center at different times, efficiently modulating fore-aft accelerations. However, during crouch gait, the quadriceps and ankle plantarflexors produce fore-aft accelerations at the same time and the opposing fore-aft accelerations generated by these muscles contribute to the inefficiency of crouch gait.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors had financial or personal conflict of interest with regard to this study. Original Article
Figures

References
-
- Wren TA, Rethlefsen S, Kay RM. Prevalence of specific gait abnormalities in children with cerebral palsy: influence of cerebral palsy subtype, age, and previous surgery. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25:79–83. - PubMed
-
- Jahnsen R, Villien L, Aamodt G, Stanghelle JK, Holm I. Musculoskeletal pain in adults with cerebral palsy compared with the general population. J Rehabil Med. 2004;36:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Graham H, Selber P. Musculoskeletal aspects of cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85:157–66. - PubMed
-
- Rose J, Gamble JG, Medeiros J, Burgos A, Haskell WL. Energy cost of walking in normal children and in those with cerebral palsy: comparison of heart rate and oxygen uptake. J Pediatr Orthop. 1989;9:276–9. - PubMed
-
- Waters RL, Mulroy S. The energy expenditure of normal and pathologic gait. Gait Posture. 1999;9:207–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

