Deficiency for the ubiquitin ligase UBE3B in a blepharophimosis-ptosis-intellectual-disability syndrome
- PMID: 23200864
- PMCID: PMC3516591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.10.011
Deficiency for the ubiquitin ligase UBE3B in a blepharophimosis-ptosis-intellectual-disability syndrome
Abstract
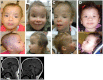
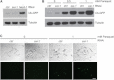
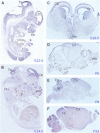
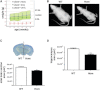
Ubiquitination plays a crucial role in neurodevelopment as exemplified by Angelman syndrome, which is caused by genetic alterations of the ubiquitin ligase-encoding UBE3A gene. Although the function of UBE3A has been widely studied, little is known about its paralog UBE3B. By using exome and capillary sequencing, we here identify biallelic UBE3B mutations in four patients from three unrelated families presenting an autosomal-recessive blepharophimosis-ptosis-intellectual-disability syndrome characterized by developmental delay, growth retardation with a small head circumference, facial dysmorphisms, and low cholesterol levels. UBE3B encodes an uncharacterized E3 ubiquitin ligase. The identified UBE3B variants include one frameshift and two splice-site mutations as well as a missense substitution affecting the highly conserved HECT domain. Disruption of mouse Ube3b leads to reduced viability and recapitulates key aspects of the human disorder, such as reduced weight and brain size and a downregulation of cholesterol synthesis. We establish that the probable Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of UBE3B, oxi-1, functions in the ubiquitin/proteasome system in vivo and is especially required under oxidative stress conditions. Our data reveal the pleiotropic effects of UBE3B deficiency and reinforce the physiological importance of ubiquitination in neuronal development and function in mammals.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kawabe H., Brose N. The role of ubiquitylation in nerve cell development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011;12:251–268. - PubMed
-
- Tai H.C., Schuman E.M. Ubiquitin, the proteasome and protein degradation in neuronal function and dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008;9:826–838. - PubMed
-
- Komander D. The emerging complexity of protein ubiquitination. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009;37:937–953. - PubMed
-
- Li W., Bengtson M.H., Ulbrich A., Matsuda A., Reddy V.A., Orth A., Chanda S.K., Batalov S., Joazeiro C.A. Genome-wide and functional annotation of human E3 ubiquitin ligases identifies MULAN, a mitochondrial E3 that regulates the organelle’s dynamics and signaling. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e1487. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

