Identification of Sox9-dependent acinar-to-ductal reprogramming as the principal mechanism for initiation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 23201164
- PMCID: PMC3568632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.10.025
Identification of Sox9-dependent acinar-to-ductal reprogramming as the principal mechanism for initiation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Tumors are largely classified by histologic appearance, yet morphologic features do not necessarily predict cellular origin. To determine the origin of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA), we labeled and traced pancreatic cell populations after induction of a PDA-initiating Kras mutation. Our studies reveal that ductal and stem-like centroacinar cells are surprisingly refractory to oncogenic transformation, whereas acinar cells readily form PDA precursor lesions with ductal features. We show that formation of acinar-derived premalignant lesions depends on ectopic induction of the ductal gene Sox9. Moreover, when concomitantly expressed with oncogenic Kras, Sox9 accelerates formation of premalignant lesions. These results provide insight into the cellular origin of PDA and suggest that its precursors arise via induction of a duct-like state in acinar cells.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


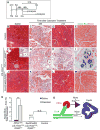
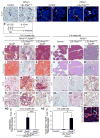
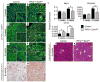

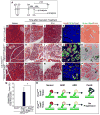
Comment in
-
Disputed paternity: the uncertain ancestry of pancreatic ductal neoplasia.Cancer Cell. 2012 Dec 11;22(6):701-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.11.015. Cancer Cell. 2012. PMID: 23238009 Free PMC article.
-
Sox9-dependent acinar-to-ductal reprogramming is critical for pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia formation.Gastroenterology. 2013 Oct;145(4):904-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.028. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23973677 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bien-Willner GA, Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. SOX9cre1, a cis-acting regulatory element located 1.1 Mb upstream of SOX9, mediates its enhancement through the SHH pathway. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:1143–1156. - PubMed
-
- Brembeck FH, Schreiber FS, Deramaudt TB, Craig L, Rhoades B, Swain G, Grippo P, Stoffers DA, Silberg DG, Rustgi AK. The mutant K-ras oncogene causes pancreatic periductal lymphocytic infiltration and gastric mucous neck cell hyperplasia in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2005–2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

