P2X₃ and TRPV1 functionally interact and mediate sensitization of trigeminal sensory neurons
- PMID: 23201260
- PMCID: PMC3600407
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.015
P2X₃ and TRPV1 functionally interact and mediate sensitization of trigeminal sensory neurons
Abstract
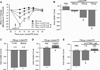
Musculoskeletal pain conditions, particularly those associated with temporomandibular disorders (TMD) affect a large percentage of the population. Identifying mechanisms underlying hyperalgesia could contribute to the development of new treatment strategies for the management of TMD and other muscle pain conditions. In this study, we provide evidence of functional interactions between two ligand-gated channels, P2X₃ and transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1), in trigeminal sensory neurons, and propose that the interactions serve as an underlying mechanism for the development of mechanical hyperalgesia. Mechanical sensitivity of the masseter muscle was assessed in lightly anesthetized rats via an electronic anesthesiometer (Ro et al., 2009). Direct intramuscular injection of a selective P2X₃ agonist, alpha,beta-methylene adenosine triphosphate (αβmeATP), induced a dose- and time-dependent hyperalgesia. Mechanical sensitivity in the contralateral muscle was unaffected suggesting local P2X₃ mediate hyperalgesia. Anesthetizing the overlying skin had no effect on αβmeATP-induced hyperalgesia confirming the contribution of P2X₃ from the muscle. Importantly, the αβmeATP-induced hyperalgesia was prevented by pretreatment of the muscle with a TRPV1 antagonist, AMG9810. P2X₃ was co-expressed with TRPV1 in the masseter muscle afferents confirming the possibility for intracellular interactions. Additionally, in a subpopulation of P2Xv/TRPV1 positive neurons, capsaicin-induced Ca(2+) transients were significantly amplified following P2X₃ activation. Finally, activation of P2X₃ induced phosphorylation of serine, but not threonine, residues in TRPV1 in trigeminal ganglia cultures. Significant phosphorylation was observed at 15 min, the time point at which behavioral hyperalgesia was prominent. Previously, activation of either P2X₃ or TRPV1 had been independently implicated in the development of mechanical hyperalgesia. Our data propose P2X₃ and TRPV1 interact in a facilitatory manner, which could contribute to the peripheral sensitization known to underlie masseter hyperalgesia.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
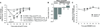
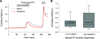


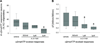


References
-
- Ambalavanar R, Moritani M, Dessem D. Trigeminal P2X3 receptor expression differs from dorsal root ganglion and is modulated by deep tissue inflammation. Pain. 2005;117:280–291. - PubMed
-
- Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM, Tsuruda PR, Basbaum AI, Stucky CL, Jordt SE, Julius D. The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature. 2007;448:204–208. - PubMed
-
- Bhave G, Zhu W, Wang H, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau RWt. cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates desensitization of the capsaicin receptor (VR1) by direct phosphorylation. Neuron. 2002;35:721–731. - PubMed
-
- Bhave G, Hu HJ, Glauner KS, Zhu W, Wang H, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau RWt. Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100:12480–12485. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

