Exercise induces age-dependent changes on epigenetic parameters in rat hippocampus: a preliminary study
- PMID: 23201423
- PMCID: PMC4405233
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2012.11.011
Exercise induces age-dependent changes on epigenetic parameters in rat hippocampus: a preliminary study
Abstract
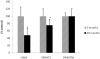
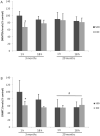
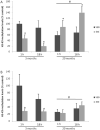
Regular exercise improves learning and memory, including during aging process. Interestingly, the imbalance of epigenetic mechanisms has been linked to age-related cognitive deficits. However, studies about epigenetic alterations after exercise during the aging process are rare. In this preliminary study we investigated the effect of aging and exercise on DNA methyltransferases (DNMT1 and DNMT3b) and H3-K9 methylation levels in hippocampus from 3 and 20-months aged Wistar rats. The animals were submitted to two exercise protocols: single session or chronic treadmill protocol. DNMT1 and H3-K9 methylation levels were decreased in hippocampus from aged rats. The single exercise session decreased both DNMT3b and DNMT1 levels in young adult rats, without any effect in the aged group. Both exercise protocols reduced H3-K9 methylation levels in young adult rats, while the single session reversed the changes on H3-K9 methylation levels induced by aging. Together, these results suggest that an imbalance on DNMTs and H3-K9 methylation levels might be linked to the brain aging process and that the outcome to exercise seems to vary through lifespan.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arida RM, Scorza FA, dos Santos NF, Peres CA, Cavalheiro EA. Effect of physical exercise on seizure occurrence in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy in rats. Epilepsy Res. 1999;37:45–52. - PubMed
-
- Brooks GA, White TP. Determination of metabolic and heart rate responses of rats to treadmill exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1978;45:1009–1015. - PubMed
-
- Chandramohan Y, Droste SK, Arthur JS, Reul JM. The forced swimming-induced behavioural immobility response involves histone H3 phospho-acetylation and c-Fos induction in dentate gyrus granule neurons via activation of the N-methyl-D aspartate/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen- and stress-activated kinase signalling pathway. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:2701–2713. - PubMed
-
- Elsner VR, Lovatel GA, Bertoldi K, Vanzella C, Santos FM, Spindler C, de Almeida EF, Nardin P, Siqueira IR. Effect of different exercise protocols on histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases activities in rat hippocampus. Neurosci. 2011;29:580–587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

