Modeling the impact of public access defibrillator range on public location cardiac arrest coverage
- PMID: 23201501
- PMCID: PMC3615148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2012.11.019
Modeling the impact of public access defibrillator range on public location cardiac arrest coverage
Abstract
Background: Public access defibrillation with automated external defibrillators (AEDs) can improve survival from out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCA) occurring in public. Increasing the effective range of AEDs may improve coverage for public location OHCAs.
Objective: To quantify the relationship between AED effective range and public location cardiac arrest coverage.
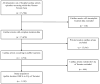
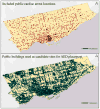
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study using the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium Epistry database. We included all public-location, atraumatic, EMS-attended OHCAs in Toronto, Canada between December 16, 2005 and July 15, 2010. We ran a mathematical model for AED placement that maximizes coverage of historical public OHCAs given pre-specified values of AED effective range and the number of locations to place AEDs. Locations of all non-residential buildings were obtained from the City of Toronto and used as candidate sites for AED placement. Coverage was evaluated for range values from 10 to 300 m and number of AED locations from 10 to 200, both in increments of 10, for a total of 600 unique scenarios. Coverage from placing AEDs in all public buildings was also measured.
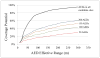
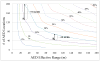
Results: There were 1310 public location OHCAs during the study period, with 25,851 non-residential buildings identified as candidate sites for AED placement. Cardiac arrest coverage increased with AED effective range, with improvements in coverage diminishing at higher ranges. For example, for a deployment of 200 AED locations, increasing effective range from 100 m to 200 m covered an additional 15% of cardiac arrests, whereas increasing range further from 200 m to 300 m covered an additional 10%. Placing an AED in each of the 25,851 public buildings resulted in coverage of 50% and 95% under assumed effective ranges of 50 m and 300 m, respectively.
Conclusion: Increasing AED effective range can improve cardiac arrest coverage. Mathematical models can help evaluate the potential impact of initiatives which increase AED range.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Weisfeldt ML, Sitlani CM, Ornato JP, Rea T, Aufderheide TP, Davis D, Dreyer J, Hess EP, Jui J, Maloney J, Sopko G, Powell J, Nichol G, Morrison LJ for the ROC Investigators. Survival after application of automatic external defibrillators before arrival of the emergency medical system: Evaluation in the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium population of 21 million. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:1713–1720. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nichol G, Stiell IG, Laupacis A, et al. A Cumulative metaanalysis of the effectiveness of defibrillator-capable emergency medical services for victims of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Ann Emerg Med. 1999;34:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Valenzuela TD, Roe DJ, Nichol G, Clark LL, Spaite DW, Hardman RG. Outcomes of rapid defibrillation by security officers after cardiac arrest in casinos. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1206–1209. - PubMed
-
- Page RL, Joglar JA, Kowal RC, Zagrodzky JD, Nelson LL, Ramaswamy K, Barbera SJ, Hamdan MH, McKenas DK. Use of automated external defibrillators by a U.S. airline. New Engl J Med. 2000;343:1210–1216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HL077866/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- HL077867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01 HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077872/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077881/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077908/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077908/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077866/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077872/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077885/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

