TRAF family member-associated NF-kappa B activator (TANK) expression increases in injured sensory neurons and is transcriptionally regulated by Sox11
- PMID: 23201825
- PMCID: PMC3558548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.034
TRAF family member-associated NF-kappa B activator (TANK) expression increases in injured sensory neurons and is transcriptionally regulated by Sox11
Abstract
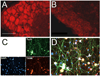
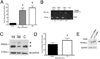
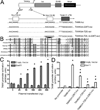
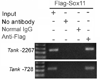
Peripheral nerve injury evokes rapid and complex changes in gene transcription and cellular signaling pathways. Understanding how these changes are functionally related is essential for developing new approaches that accelerate and improve nerve regeneration. Toward this goal we found that nerve injury induces a rapid and significant up-regulation of the transcription factor Sox11 in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons. Gain and loss of function studies have shown this increase is essential for normal axon regeneration. To determine how Sox11 impacts neuronal gene expression, DRG neurons were treated with Sox11 siRNA to identify potential transcriptional targets. One gene significantly reduced by Sox11 knockdown was TRAF (tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor)-associated NF-κB activator (TANK). Here we show that TANK is expressed in DRG neurons, that TANK expression is increased in response to peripheral nerve injury and that Sox11 overexpression in vitro increases TANK expression. Injury and in vitro overexpression were also found to preferentially increase TANK transcript variant 3 and a larger TANK protein isoform. To determine if Sox11 regulates TANK transcription bioinformatic analysis was used to identify potential Sox-binding motifs within 5kbp of the TANK 5' untranslated region (UTR) across several mammalian genomes. Two sites in the mouse TANK gene were examined. Luciferase expression assays coupled with site-directed mutagenesis showed each site contributes to enhanced TANK promoter activity. In addition, chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed direct Sox11 binding in regions containing the two identified Sox motifs in the mouse TANK 5'-UTR. These studies are the first to show that TANK is expressed in DRG neurons, that TANK is increased by peripheral nerve injury and that the regulation of TANK expression is, at least in part, controlled by the injury-associated transcription factor Sox11.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SRY-box containing gene 11 (Sox11) transcription factor is required for neuron survival and neurite growth.Neuroscience. 2006 Dec 1;143(2):501-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.010. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 17055661 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Sox11 promotes nerve regeneration through activation of the regeneration-associated gene Sprr1a.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jan;233(1):221-32. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22024412 Free PMC article.
-
Sox11 transcription factor modulates peripheral nerve regeneration in adult mice.Brain Res. 2009 Feb 23;1256:43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.12.032. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19133245 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of Transcription Factor SRY-box-Containing Gene 11 (Sox11) Enhances Neurite Growth by Regulating Neurotrophic Factor Responsiveness.Neuroscience. 2018 Jul 1;382:93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.037. Epub 2018 May 8. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29746989 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Sox11 promotes corticospinal tract regeneration after spinal injury while interfering with functional recovery.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 18;35(7):3139-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2832-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25698749 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Voluntary Exercise Positively Affects the Recovery of Long-Nerve Gap Injury Following Tube-Bridging with Human Skeletal Muscle-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation.J Clin Med. 2018 Apr 2;7(4):67. doi: 10.3390/jcm7040067. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 29614796 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathic pain development following nerve injury is mediated by SOX11-ARID1A-SOCS3 transcriptional regulation in the spinal cord.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 7;51(1):281. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09183-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38324208
-
Advances and Future Applications of Augmented Peripheral Nerve Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 7;17(9):1494. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091494. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27618010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis of trigeminal ganglia following masseter muscle inflammation in rats.Mol Pain. 2016 Oct 4;12:1744806916668526. doi: 10.1177/1744806916668526. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27702909 Free PMC article.
-
The Cortical Neuroimmune Regulator TANK Affects Emotional Processing and Enhances Alcohol Drinking: A Translational Study.Cereb Cortex. 2019 Apr 1;29(4):1736-1751. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy341. Cereb Cortex. 2019. PMID: 30721969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernard P, Harley VR. Acquisition of SOX transcription factor specificity through protein-protein interaction, modulation of Wnt signalling and post-translational modification. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:400–410. - PubMed
-
- Chao AT, Jones WM, Bejsovec A. The HMG-box transcription factor SoxNeuro acts with Tcf to control Wg/Wnt signaling activity. Development. 2007;134:989–997. - PubMed
-
- Chariot A, Leonardi A, Muller J, Bonif M, Brown K, Siebenlist U. Association of the adaptor TANK with the I kappa B kinase (IKK) regulator NEMO connects IKK complexes with IKK epsilon and TBK1 kinases. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:37029–37036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

