Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrene-cadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato
- PMID: 23201830
- PMCID: PMC3528031
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ers323
Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrene-cadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato
Abstract
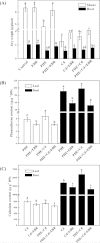
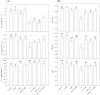
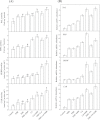
Heavy metal pollution often occurs together with organic contaminants. Brassinosteroids (BRs) induce plant tolerance to several abiotic stresses, including phenanthrene (PHE) and cadmium (Cd) stress. However, the role of BRs in PHE+Cd co-contamination-induced stress amelioration is unknown. Here, the interactive effects of PHE, Cd, and 24-epibrassinolide (EBR; a biologically active BR) were investigated in tomato plants. The application of Cd (100 µM) alone was more phytotoxic than PHE applied alone (100 µM); however, their combined application resulted in slightly improved photosynthetic activity and pigment content compared with Cd alone after a 40 d exposure. Accumulation of reactive oxygen species and membrane lipid peroxidation were induced by PHE and/or Cd; however, the differences in effect were insignificant between Cd and PHE+Cd. The foliar application of EBR (0.1 µM) to PHE- and/or Cd-stressed plants alleviated photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress by causing enhancement of the activity of the enzymes and related transcript levels of the antioxidant system, secondary metabolism, and the xenobiotic detoxification system. Additionally, PHE and/or Cd residues were significantly decreased in both the leaves and roots after application of EBR, more specifically in PHE+Cd-stressed plants when treated with EBR, indicating a possible improvement in detoxification of these pollutants. The findings thus suggest a potential interaction of EBR and PHE for Cd stress alleviation. These results advocate a positive role for EBR in reducing pollutant residues for food safety and also strengthening phytoremediation.
Figures



References
-
- Ahammed GJ, Gao CJ, Ogweno JO, Zhou YH, Xia XJ, Mao WH, Shi K, Yu JQ. 2012. a Brassinosteroids induce plant tolerance against phenanthrene by enhancing degradation and detoxification in Solanum lycopersicum L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 80, 28–36 . - PubMed
-
- Ahammed GJ, Yuan HL, Ogweno JO, Zhou YH, Xia XJ, Mao WH, Shi K, Yu JQ. 2012. b Brassinosteroid alleviates phenanthrene and pyrene phytotoxicity by increasing detoxification activity and photosynthesis in tomato. Chemosphere. 86, 546–555 . - PubMed
-
- Alkio M, Tabuchi TM, Wang XC, Colón-Carmona A. 2005. Stress responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Arabidopsis include growth inhibition and hypersensitive response-like symptoms. Journal of Experimental Botany. 56, 2983–2994 . - PubMed
-
- Babu TS, Marder JB, Tripuranthakam S, Dixon DG, Greenberg BM. 2001. Synergistic effects of a photooxidized polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and copper on photosynthesis and plant growth: evidence that in vivo formation of reactive oxygen species is a mechanism of copper toxicity. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 20, 1351–1358 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

