Development of a respiratory inductive plethysmography module supporting multiple sensors for wearable systems
- PMID: 23201991
- PMCID: PMC3545562
- DOI: 10.3390/s121013167
Development of a respiratory inductive plethysmography module supporting multiple sensors for wearable systems
Abstract
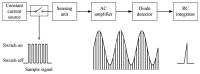
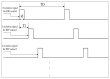
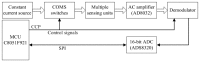
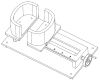
In this paper, we present an RIP module with the features of supporting multiple inductive sensors, no variable frequency LC oscillator, low power consumption, and automatic gain adjustment for each channel. Based on the method of inductance measurement without using a variable frequency LC oscillator, we further integrate pulse amplitude modulation and time division multiplexing scheme into a module to support multiple RIP sensors. All inductive sensors are excited by a high-frequency electric current periodically and momentarily, and the inductance of each sensor is measured during the time when the electric current is fed to it. To improve the amplitude response of the RIP sensors, we optimize the sensing unit with a matching capacitor parallel with each RIP sensor forming a frequency selection filter. Performance tests on the linearity of the output with cross-sectional area and the accuracy of respiratory volume estimation demonstrate good linearity and accurate lung volume estimation. Power consumption of this new RIP module with two sensors is very low. The performance of respiration measurement during movement is also evaluated. This RIP module is especially desirable for wearable systems with multiple RIP sensors for long-term respiration monitoring.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Low power wireless acquisition module for wearable health monitoring systems.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:704-7. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5626161. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010. PMID: 21095668
-
Estimating actigraphy from motion artifacts in ECG and respiratory effort signals.Physiol Meas. 2016 Jan;37(1):67-82. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/37/1/67. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Physiol Meas. 2016. PMID: 26641863
-
Enhanced Breathing Pattern Detection during Running Using Wearable Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 20;21(16):5606. doi: 10.3390/s21165606. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451048 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Respiratory Sensor Solutions to Support Patient Diagnosis and Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;25(4):1078. doi: 10.3390/s25041078. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wearable Sensors? What is there to sense?Stud Health Technol Inform. 2005;117:80-8. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2005. PMID: 16282656 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Respiration Types Through Respiratory Signal Derived From Clinical and Wearable Electrocardiograms.IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023 Dec 15;4:268-274. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2023.3343557. eCollection 2023. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 38196981 Free PMC article.
-
A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 29;23(15):6790. doi: 10.3390/s23156790. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571572 Free PMC article.
-
Chronotropic Competence Indices Extracted from Wearable Sensors for Cardiovascular Diseases Management.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Oct 25;17(11):2441. doi: 10.3390/s17112441. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29068357 Free PMC article.
-
Paediatric sleep diagnostics in the 21st century: the era of "sleep-omics"?Eur Respir Rev. 2024 Jun 26;33(172):240041. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0041-2024. Print 2024 Apr. Eur Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 38925792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validity analysis of respiratory events of polysomnography using a plethysmography chest and abdominal belt.Sleep Breath. 2020 Mar;24(1):127-134. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01940-1. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Sleep Breath. 2020. PMID: 31667682
References
-
- Carry P.Y., Baconnier P., Eberhard A., Cotte P., Benchetrit G. Evaluation of respiratory inductive plethysmography: Accuracy for analysis of respiratory waveforms. Chest. 1997;111:910–915. - PubMed
-
- Fiamma M.N., Samara Z., Baconnier P., Similowski T., Straus C. Respiratory inductive plethysmography to assess respiratory variability and complexity in humans. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007;156:234–239. - PubMed
-
- Bradley J., Kent M.L., O'Neill B., Nevill A., Boyle L., Elborn J.S. Cardiorespiratory measurements during field tests in CF: Use of an ambulatory monitoring system. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011;46:253–260. - PubMed
-
- Iber C., Ancoli-Israel S., Chesson A., Quan S. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications. 1st ed. American Academy of Sleep Medicine; Westchester, IL, USA: 2007.
-
- Grossman P. The LifeShirt: A multi-function ambulatory system monitoring health, disease, and medical intervention in the real world. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2004;108:133–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

