Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 23202738
- PMCID: PMC3533531
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI60658
Molecular pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
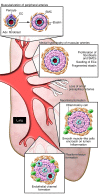
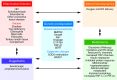
Recent clinical and experimental studies are redefining the cellular and molecular bases of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The genetic abnormalities first identified in association with the idiopathic form of PAH--together with a vast increase in our understanding of cell signaling, cell transformation, and cell-cell interactions; gene expression; microRNA processing; and mitochondrial and ion channel function--have helped explain the abnormal response of vascular cells to injury. Experimental and clinical studies now converge on the intersection and interactions between a genetic predisposition involving the BMPR2 signaling pathway and an impaired metabolic and chronic inflammatory state in the vessel wall. These deranged processes culminate in an exuberant proliferative response that occludes the pulmonary arterial (PA) lumen and obliterates the most distal intraacinar vessels. Here, we describe emerging therapies based on preclinical studies that address these converging pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Rabinovitch M, et al. Pulmonary artery endothelial abnormalities in patients with congenital heart defects and pulmonary hypertension: A correlation of light with scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1986;55(6):632–653. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg HC, Rabinovitch M. Endothelial injury and vascular reactivity in monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1988;255(6 pt 2):H1484–H1491. - PubMed
-
- Thompson K, Rabinovitch M. Exogenous leukocyte and endogenous elastases can mediate mitogenic activity in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by release of extracellular-matrix bound basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1996;166(3):495–505. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199603)166:3<495::AID-JCP4>3.0.CO;2-K. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

