Interferon-β1b increases Th2 response in neuromyelitis optica
- PMID: 23202893
- PMCID: PMC3497267
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms131012213
Interferon-β1b increases Th2 response in neuromyelitis optica
Abstract
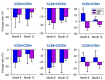
A Japanese randomized controlled study showed that Interferon â (IFN-â1b) therapy is clinically effective in decreasing the frequency of attacks in multiple sclerosis (MS), even in optico-spinal MS (OSMS). However, recent studies have shown that IFN-â (IFN-â1a/IFN-â1b) treatment was not effective in neuromyelitis optica (NMO) patients and that the diminished benefit of IFN-â treatment in NMO may be due to different immune responses to IFN-â. We determined longitudinally the expression of CCR5, CXCR3 and CCR4 on CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells in the blood from patients with NMO and MS treated with IFN-â1b. During a 12-month period of IFN-â1b therapy, the annualized relapse rate decreased in MS patients but not in NMO patients. There was no significant difference in the expression of the chemokine receptors between NMO and MS at baseline. The percentages of CD4+CCR5+ and CD4+CXCR3+ T cells, representative of the Th1 response, were decreased in both NMO and MS after treatment. The percentage of CD4+CCR4+ T cells, representative of the Th2 response, was decreased in MS, but those for NMO was significantly increased compared with the pretreatment levels. Our results indicate that IFN-â1b-induced up-modulation of the Th2 response in NMO patients may be the source of differences in the therapeutic response to IFN-â1b therapy. In the present study, Th2 predominance is involved in the pathogenesis of NMO.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Th1/Th2-related chemokine receptors in peripheral T cells with disease activity in patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica.Eur Neurol. 2011;66(2):91-7. doi: 10.1159/000329576. Epub 2011 Aug 12. Eur Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21846991
-
Expression of chemokine receptors on peripheral blood lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica.BMC Neurol. 2010 Nov 11;10:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-10-113. BMC Neurol. 2010. PMID: 21067621 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophosphamide modulates CD4+ T cells into a T helper type 2 phenotype and reverses increased IFN-gamma production of CD8+ T cells in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.J Neuroimmunol. 2004 Jan;146(1-2):189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2003.10.036. J Neuroimmunol. 2004. PMID: 14698862
-
[Chemokines and chemokine receptors in multiple sclerosis].Nihon Rinsho. 2003 Aug;61(8):1422-7. Nihon Rinsho. 2003. PMID: 12962033 Review. Japanese.
-
Neuromyelitis optica and asian phenotype of multiple sclerosis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Oct;1142:58-71. doi: 10.1196/annals.1444.002. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 18990121 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemokines and chemokine receptors in multiple sclerosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:659206. doi: 10.1155/2014/659206. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24639600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The levels of circulating cytokines and risk of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 1;15:1418309. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1418309. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39011048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sørensen T.L., Sellebjerg F. Selective suppression of chemokine receptor CXCR3 expression by interferon-beta1a in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2002;8:104–107. - PubMed
-
- Sega S., Wraber B., Mesec A., Horvat A., Ihan A. IFN-beta1a and IFN-beta1b have different patterns of influence on cytokines. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2004;106:255–258. - PubMed
-
- Ersoy E., Kuş C.N., Sener U., Coker I., Zorlu Y. The effects of interferon-beta on interleukin-10 in multiple sclerosis patients. Eur. J. Neurol. 2005;12:208–211. - PubMed
-
- Krakauer M., Sorensen P.S., Khademi M., Olsson T., Sellebjerg F. Dynamic T-lymphocyte chemokine receptor expression induced by interferon-beta therapy in multiple sclerosis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006;64:155–163. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu Y., Ota K., Kubo S., Kabasawa C., Kobayashi M., Ohashi T., Uchiyama S. Association of Th1/Th2-related chemokine receptors in peripheral T cells with disease activity in patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Eur. Neurol. 2011;66:91–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials