Syncope in a patient being treated for hepatic and intestinal amoebiasis
- PMID: 23203174
- PMCID: PMC4543832
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006687
Syncope in a patient being treated for hepatic and intestinal amoebiasis
Abstract
A 63-year-old man presented to our hospital with amoebic liver abscess and was treated successfully for the same. During the course of his treatment, he developed syncopal attacks and was found to have Torsades de Pointes on electrocardiogram. The patient was treated with intravenous magnesium and direct current cardioversion. Hypokalaemia, chloroquine and sepsis were suspected to have precipitated the arrhythmia. The patient remained arrhythmia-free following the correction of these factors.
Figures
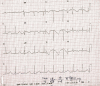
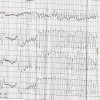
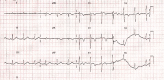
References
-
- Haverkamp W, Hördt M, Chen X, et al. Torsade de pointes. Z Kardiol 1993;82:763–74. - PubMed
-
- Roden DM. Torsade de pointes. Clin Cardiol 1993;16:683–6. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz PJ, Moss AJ, Vincent GM. Diagnostic criteria for the long QT syndrome: an update. Circulation 1993;88:782–4. - PubMed
-
- Harris L, Downar E, Shaikh NA, et al. Antiarrhythmic potential of chloroquine: New use for an old drug. Can J Cardiol 1988;4:295–300. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez-Chapula J, Salinas-Stefanon E, Torres-Jácome J. Blockade of currents by the antimalarial drug chloroquine in feline ventricular myocytes. JPET 2001;297:437–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
