Base excision repair in physiology and pathology of the central nervous system
- PMID: 23203191
- PMCID: PMC3546685
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms131216172
Base excision repair in physiology and pathology of the central nervous system
Abstract
Relatively low levels of antioxidant enzymes and high oxygen metabolism result in formation of numerous oxidized DNA lesions in the tissues of the central nervous system. Accumulation of damage in the DNA, due to continuous genotoxic stress, has been linked to both aging and the development of various neurodegenerative disorders. Different DNA repair pathways have evolved to successfully act on damaged DNA and prevent genomic instability. The predominant and essential DNA repair pathway for the removal of small DNA base lesions is base excision repair (BER). In this review we will discuss the current knowledge on the involvement of BER proteins in the maintenance of genetic stability in different brain regions and how changes in the levels of these proteins contribute to aging and the onset of neurodegenerative disorders.
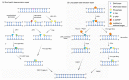
Figures
References
-
- Lindahl T. Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature. 1993;362:709–715. - PubMed
-
- Van Loon B., Markkanen E., Hubscher U. Oxygen as a friend and enemy: How to combat the mutational potential of 8-oxo-guanine. DNA Repair. 2010;9:604–616. - PubMed
-
- Magistretti P.J., Pellerin L. Cellular bases of brain energy metabolism and their relevance to functional brain imaging: Evidence for a prominent role of astrocytes. Cerebr. Cortex. 1996;6:50–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

