Translational applications of evaluating physiologic variability in human endotoxemia
- PMID: 23203205
- PMCID: PMC3664105
- DOI: 10.1007/s10877-012-9418-1
Translational applications of evaluating physiologic variability in human endotoxemia
Abstract
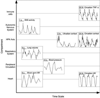
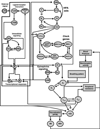
Dysregulation of the inflammatory response is a critical component of many clinically challenging disorders such as sepsis. Inflammation is a biological process designed to lead to healing and recovery, ultimately restoring homeostasis; however, the failure to fully achieve those beneficial results can leave a patient in a dangerous persistent inflammatory state. One of the primary challenges in developing novel therapies in this area is that inflammation is comprised of a complex network of interacting pathways. Here, we discuss our approaches towards addressing this problem through computational systems biology, with a particular focus on how the presence of biological rhythms and the disruption of these rhythms in inflammation may be applied in a translational context. By leveraging the information content embedded in physiologic variability, ranging in scale from oscillations in autonomic activity driving short-term heart rate variability to circadian rhythms in immunomodulatory hormones, there is significant potential to gain insight into the underlying physiology.
Figures
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(16):1546–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

