EENdb: a database and knowledge base of ZFNs and TALENs for endonuclease engineering
- PMID: 23203870
- PMCID: PMC3531095
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1144
EENdb: a database and knowledge base of ZFNs and TALENs for endonuclease engineering
Abstract
We report here the construction of engineered endonuclease database (EENdb) (http://eendb.zfgenetics.org/), a searchable database and knowledge base for customizable engineered endonucleases (EENs), including zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) and transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs). EENs are artificial nucleases designed to target and cleave specific DNA sequences. EENs have been shown to be a very useful genetic tool for targeted genome modification and have shown great potentials in the applications in basic research, clinical therapies and agricultural utilities, and they are specifically essential for reverse genetics research in species where no other gene targeting techniques are available. EENdb contains over 700 records of all the reported ZFNs and TALENs and related information, such as their target sequences, the peptide components [zinc finger protein-/transcription activator-like effector (TALE)-binding domains, FokI variants and linker peptide/framework], the efficiency and specificity of their activities. The database also lists EEN engineering tools and resources as well as information about forms and types of EENs, EEN screening and construction methods, detection methods for targeting efficiency and many other utilities. The aim of EENdb is to represent a central hub for EEN information and an integrated solution for EEN engineering. These studies may help to extract in-depth properties and common rules regarding ZFN or TALEN efficiency through comparison of the known ZFNs or TALENs.
Figures
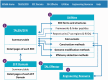

References
-
- Baker M. Gene-editing nucleases. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:23–26. - PubMed
-
- Xiao A, Hu YY, Wang WY, Yang ZP, Wang ZX, Huang P, Tong XJ, Zhang B, Lin S. Progress in zinc finger nuclease engineering for targeted genome modification. Hereditas. 2011;33:665–683. - PubMed
-
- Huang P, Zhu Z, Lin S, Zhang B. Reverse genetic approaches in zebrafish. J. Genet. Genomics. 2012;39:421–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

