TCMID: Traditional Chinese Medicine integrative database for herb molecular mechanism analysis
- PMID: 23203875
- PMCID: PMC3531123
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1100
TCMID: Traditional Chinese Medicine integrative database for herb molecular mechanism analysis
Abstract
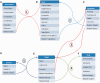
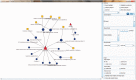
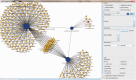
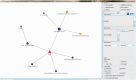
As an alternative to modern western medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is receiving increasingly attention worldwide. Great efforts have been paid to TCM's modernization, which tries to bridge the gap between TCM and modern western medicine. As TCM and modern western medicine share a common aspect at molecular level that the compound(s) perturb human's dysfunction network and restore human normal physiological condition, the relationship between compounds (in herb, refer to ingredients) and their targets (proteins) should be the key factor to connect TCM and modern medicine. Accordingly, we construct this Traditional Chinese Medicine Integrated Database (TCMID, http://www.megabionet.org/tcmid/), which records TCM-related information collected from different resources and through text-mining method. To enlarge the scope of the TCMID, the data have been linked to common drug and disease databases, including Drugbank, OMIM and PubChem. Currently, our TCMID contains ∼47 000 prescriptions, 8159 herbs, 25 210 compounds, 6828 drugs, 3791 diseases and 17 521 related targets, which is the largest data set for related field. Our web-based software displays a network for integrative relationships between herbs and their treated diseases, the active ingredients and their targets, which will facilitate the study of combination therapy and understanding of the underlying mechanisms for TCM at molecular level.
Figures
References
-
- Qiu J. Traditional medicine—a culture in the balance. Nature. 2007;448:126–128. - PubMed
-
- Qiu J. China plans to modernize traditional medicine. Nature. 2007;446:590–591. - PubMed
-
- Normile D. Asian medicine. The new face of traditional Chinese medicine. Science. 2003;299:188–190. - PubMed
-
- Xue TH, Roy R. Studying traditional Chinese medicine. Science. 2003;300:740–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

