Factorbook.org: a Wiki-based database for transcription factor-binding data generated by the ENCODE consortium
- PMID: 23203885
- PMCID: PMC3531197
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1221
Factorbook.org: a Wiki-based database for transcription factor-binding data generated by the ENCODE consortium
Abstract
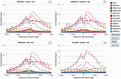
The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) consortium aims to identify all functional elements in the human genome including transcripts, transcriptional regulatory regions, along with their chromatin states and DNA methylation patterns. The ENCODE project generates data utilizing a variety of techniques that can enrich for regulatory regions, such as chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), micrococcal nuclease (MNase) digestion and DNase I digestion, followed by deeply sequencing the resulting DNA. As part of the ENCODE project, we have developed a Web-accessible repository accessible at http://factorbook.org. In Wiki format, factorbook is a transcription factor (TF)-centric repository of all ENCODE ChIP-seq datasets on TF-binding regions, as well as the rich analysis results of these data. In the first release, factorbook contains 457 ChIP-seq datasets on 119 TFs in a number of human cell lines, the average profiles of histone modifications and nucleosome positioning around the TF-binding regions, sequence motifs enriched in the regions and the distance and orientation preferences between motif sites.
Figures


References
-
- Mardis ER, Mardis ER. ChIP-seq: welcome to the new frontier. Nat. Methods. 2007;4:613–614. - PubMed
-
- Robertson G, Hirst M, Bainbridge M, Bilenky M, Zhao Y, Zeng T, Euskirchen G, Bernier B, Varhol R, Delaney A, et al. Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2007;4:651–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

