Long-term immunogenicity of hepatitis A virus vaccine in Alaska 17 years after initial childhood series
- PMID: 23204169
- PMCID: PMC3611760
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis710
Long-term immunogenicity of hepatitis A virus vaccine in Alaska 17 years after initial childhood series
Abstract
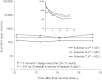
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends hepatitis A virus (HAV) vaccination for all children at age 1 year and for high-risk adults. The vaccine is highly effective; however, protection duration is unknown. We report HAV antibody concentrations 17 years after childhood immunization, demonstrating that protective antibody levels remain and have stabilized over the past 7 years.
Figures
References
-
- Bulkow LR, Wainwright RB, McMahon BJ, Middaugh JP, Jenkerson SA, Margolis HS. Secular trends in hepatitis A virus infection among Alaska Natives. J Infect Dis. 1993;168:1017–20. - PubMed
-
- Peach D, McMahon BJ, Bulkow L, Funk E, Harpaz R, Margolis HS. Impact of recurrent epidemics of hepatitis a virus infection on population immunity levels: Bristol Bay, Alaska. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1081–5. - PubMed
-
- McMahon BJ, Beller M, Williams J, Schloss M, Tanttila H, Bulkow L. A program to control an outbreak of hepatitis A in Alaska by using an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1996;150:733–9. - PubMed
-
- Hammitt LL, Bulkow L, Hennessy TW, et al. Persistence of antibody to hepatitis A virus 10 years after vaccination among children and adults. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:1776–82. - PubMed
-
- Byrd KK, Bruden DL, Bruce MG, et al. Long-term immunogenicity of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: Follow-up at 15 years. J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2010;5:321–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

