Diabetic atherosclerosis in APOE*4 mice: synergy between lipoprotein metabolism and vascular inflammation
- PMID: 23204275
- PMCID: PMC3588868
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M031435
Diabetic atherosclerosis in APOE*4 mice: synergy between lipoprotein metabolism and vascular inflammation
Abstract
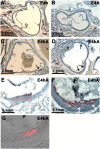
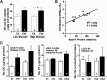
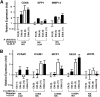
Diabetes is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. To examine how diabetes interacts with a mildly compromised lipid metabolism, we introduced the diabetogenic Ins2(C96Y/+) (Akita) mutation into mice expressing human apoE4 (E4) combined with either an overexpressing human LDL receptor gene (hLDLR) or the wild-type mouse gene. The hLDLR allele caused 2-fold reductions in plasma HDL-cholesterol, plasma apoA1, and hepatic triglyceride secretion. Diabetes increased plasma total cholesterol 1.3-fold and increased apoB48 secretion 3-fold, while reducing triglyceride secretion 2-fold. Consequently, diabetic E4 mice with hLDLR secrete increased numbers of small, cholesterol-enriched, apoB48-containing VLDL, although they have near normal plasma cholesterol (<120 mg/dl). Small foam cell lesions were present in the aortic roots of all diabetic E4 mice with hLDLR that we analyzed at six months of age. None were present in nondiabetic mice or in diabetic mice without hLDLR. Aortic expression of genes affecting leukocyte recruitment and adhesion was enhanced by diabetes. ApoA1 levels, but not diabetes, were strongly correlated with the ability of plasma to efflux cholesterol from macrophages. We conclude that the diabetes-induced proinflammatory changes in the vasculature and the hLDLR-mediated cholesterol accumulation in macrophages synergistically trigger atherosclerosis in mice with human apoE4, although neither alone is sufficient.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spontaneously diabetic Ins2(+/Akita):apoE-deficient mice exhibit exaggerated hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jul;301(1):E145-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00034.2011. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21447785 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 exaggerates diabetic dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis in mice lacking the LDL receptor.Diabetes. 2011 Sep;60(9):2285-94. doi: 10.2337/db11-0466. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21810592 Free PMC article.
-
ABCA1 overexpression in the liver of LDLr-KO mice leads to accumulation of pro-atherogenic lipoproteins and enhanced atherosclerosis.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 3;281(44):33053-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604526200. Epub 2006 Aug 23. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16928680
-
Apolipoprotein E in lipoprotein metabolism, health and cardiovascular disease.Pathology. 2019 Feb;51(2):165-176. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2018.11.002. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Pathology. 2019. PMID: 30598326 Review.
-
Triglyceride Rich Lipoprotein -LPL-VLDL Receptor and Lp(a)-VLDL Receptor Pathways for Macrophage Foam Cell Formation.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017 Jun 1;24(6):552-559. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17004. Epub 2017 Apr 19. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017. PMID: 28428482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation: Bridging Age, Menopause and APOEε4 Genotype to Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Oct 9;10:312. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00312. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30356809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of diabetic macrovascular complications: key players in the development of new therapeutic approaches.J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:404085. doi: 10.1155/2015/404085. Epub 2015 Feb 15. J Diabetes Res. 2015. PMID: 25785279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin Reduces Cognitive Deficits by Inhibiting Neuroinflammation through the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Apolipoprotein E4 Transgenic Mice.ACS Omega. 2021 Mar 2;6(10):6654-6662. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c04810. eCollection 2021 Mar 16. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33748578 Free PMC article.
-
2013 Russell Ross memorial lecture in vascular biology: cellular and molecular mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Apr;34(4):705-14. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301928. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24665124 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4 mediates insulin resistance-associated cerebrovascular dysfunction and the post-prandial response.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 May;39(5):770-781. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17746186. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 29215310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2011. National Diabetes Fact Sheet: National Estimates and General Information on Diabetes and Prediabetes in the United States, 2011. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA.
-
- Kannel W. B., McGee D. L. 1979. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: the Framingham Study. JAMA. 241: 2035–2038 - PubMed
-
- Grundy S. M., Benjamin I. J., Burke G. L., Chait A., Eckel R. H., Howard B. V., Mitch W., Smith S. C., Jr., Sowers J. R. 1999. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 100: 1134–1146 - PubMed
-
- Goldberg I. J. 2001. Clinical review 124: Diabetic dyslipidemia: causes and consequences. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86: 965–971 - PubMed
-
- Jenkins A. J., Lyons T. J., Zheng D., Otvos J. D., Lackland D. T., McGee D., Garvey W. T., Klein R. L. ; DCC/EDIC Research Group 2003. Serum lipoproteins in the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes intervention and complications cohort: associations with gender and glycemia. Diabetes Care. 26: 810–818 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

