Thrombin-cleaved fragments of osteopontin are overexpressed in malignant glial tumors and provide a molecular niche with survival advantage
- PMID: 23204518
- PMCID: PMC3561533
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.362954
Thrombin-cleaved fragments of osteopontin are overexpressed in malignant glial tumors and provide a molecular niche with survival advantage
Abstract
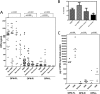
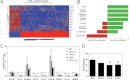
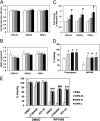
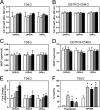
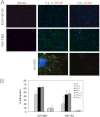
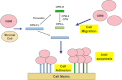
Osteopontin (OPN), which is highly expressed in malignant glioblastoma (GBM), possesses inflammatory activity modulated by proteolytic cleavage by thrombin and plasma carboxypeptidase B2 (CPB2) at a highly conserved cleavage site. Full-length OPN (OPN-FL) was elevated in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from all cancer patients compared with noncancer patients. However, thrombin-cleaved OPN (OPN-R) and thrombin/CPB2-double-cleaved OPN (OPN-L) levels were markedly increased in GBM and non-GBM gliomas compared with systemic cancer and noncancer patients. Cleaved OPN constituted ∼23 and ∼31% of the total OPN in the GBM and non-GBM CSF samples, respectively. OPN-R was also elevated in GBM tissues. Thrombin-antithrombin levels were highly correlated with cleaved OPN, but not OPN-FL, suggesting that the cleaved OPN fragments resulted from increased thrombin and CPB2 in this extracellular compartment. Levels of VEGF and CCL4 were increased in CSF of GBM and correlated with the levels of cleaved OPN. GBM cell lines were more adherent to OPN-R and OPN-L than OPN-FL. Adhesion to OPN altered gene expression, in particular genes involved with cellular processes, cell cycle regulation, death, and inflammation. OPN and its cleaved forms promoted motility of U-87 MG cells and conferred resistance to apoptosis. Although functional mutation of the RGD motif in OPN largely abolished these functions, OPN(RAA)-R regained significant cell binding and signaling function, suggesting that the SVVYGLR motif in OPN-R may substitute for the RGD motif if the latter becomes inaccessible. OPN cleavage contributes to GBM development by allowing more cells to bind in niches where they acquire anti-apoptotic properties.
Figures



References
-
- Han M. H., Hwang S. I., Roy D. B., Lundgren D. H., Price J. V., Ousman S. S., Fernald G. H., Gerlitz B., Robinson W. H., Baranzini S. E., Grinnell B. W., Raine C. S., Sobel R. A., Han D. K., Steinman L. (2008) Proteomic analysis of active multiple sclerosis lesions reveals therapeutic targets. Nature 451, 1076–1081 - PubMed
-
- Wang K. X., Denhardt D. T. (2008) Osteopontin. Role in immune regulation and stress responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 19, 333–345 - PubMed
-
- El-Tanani M. K., Campbell F. C., Kurisetty V., Jin D., McCann M., Rudland P. S. (2006) The regulation and role of osteopontin in malignant transformation and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17, 463–474 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

